Gene activator protein F006 / 9269
![]()

Wall Art and Photo Gifts from Science Photo Library
Gene activator protein F006 / 9269
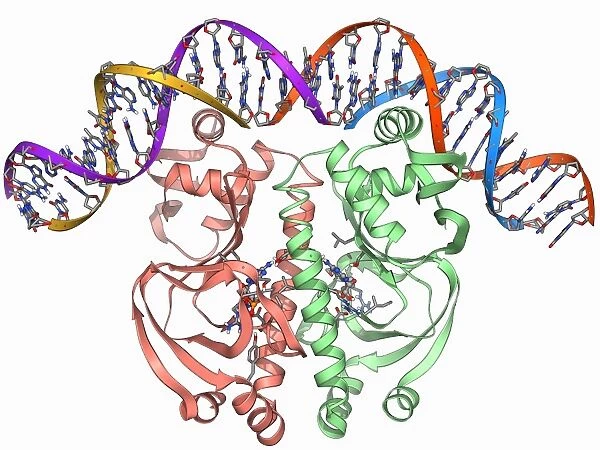
Gene activator protein. Molecular model of catabolite gene activator protein (CAP, pink and green) bound to a molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA, across top). CAP activates genes that enable bacteria to use an alternative energy source when glucose, the preferred energy source, is unavailable. Falling levels of glucose cause an increase in the messenger molecule cAMP, which binds to CAP enabling CAP to bind to DNA. cAMP binds at 2 sites either side of the centre of the CAP molecule. CAP binds to DNA at specific sites, causing it to bend. This enhances the ability of the enzyme RNA polymerase to make mRNA copies of the targeted gene
Science Photo Library features Science and Medical images including photos and illustrations
Media ID 9253353
© LAGUNA DESIGN/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Activating Alpha Helix Alternative Bacterial Bending Beta Sheet Binding Catabolite Gene Activator Dimer Double Helix Energy Source Genetic Genetic Switch Glucose Helical Lac Operon Microbiology Nucleic Acid Positive Control Proteomics Regulatory Protein Strand Strands Tertiary Structure Transcriptional Control Biochemical Biochemistry Cutouts Deoxyribonucleic Acid Genetics Microbiological Molecular Molecular Model Molecular Structure Protein
EDITORS COMMENTS
This print showcases the gene activator protein F006/9269, a crucial component in bacterial energy regulation. In this molecular model, we see the catabolite gene activator protein (CAP) bound to a DNA molecule across the top. CAP plays a vital role in activating genes that enable bacteria to utilize alternative energy sources when glucose is scarce. The mechanism behind CAP's activation lies in falling levels of glucose, which trigger an increase in the messenger molecule cAMP. This binding of cAMP allows CAP to attach itself to specific sites on DNA, causing it to bend and enhancing the enzyme RNA polymerase's ability to create mRNA copies of targeted genes. The intricate structure of CAP is illustrated with pink and green colors against a white background. The alpha helix and beta sheet formations within its tertiary structure are clearly visible, emphasizing its importance as a regulatory protein involved in transcriptional control. This artwork not only highlights the biochemical intricacies at play but also underscores the significance of genetic switches like lac operon for bacterial survival. With applications ranging from medicine to genetics research, this image serves as a valuable resource for scientists exploring proteomics, microbiology, biochemistry, and more. LAGUNA DESIGN/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY has expertly captured this scientific marvel through their meticulous attention to detail and precise cutouts. It offers us an insightful glimpse into the fascinating world of molecular biology while reminding us of nature's ingenious mechanisms for adapting to changing environments.
MADE IN THE USA
Safe Shipping with 30 Day Money Back Guarantee
FREE PERSONALISATION*
We are proud to offer a range of customisation features including Personalised Captions, Color Filters and Picture Zoom Tools
SECURE PAYMENTS
We happily accept a wide range of payment options so you can pay for the things you need in the way that is most convenient for you
* Options may vary by product and licensing agreement. Zoomed Pictures can be adjusted in the Cart.