Motility Collection
Motility, the driving force behind cellular movement and locomotion, is a captivating phenomenon that unveils the intricate world of cell structure
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
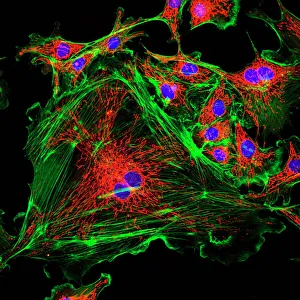
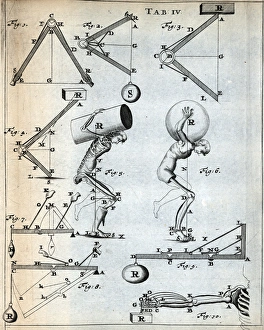
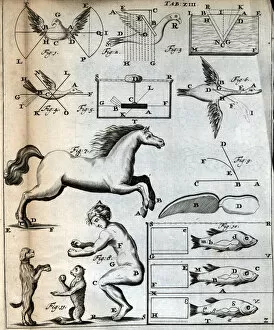
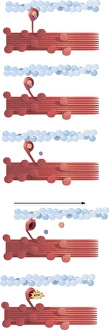
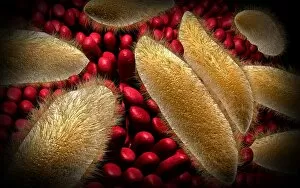
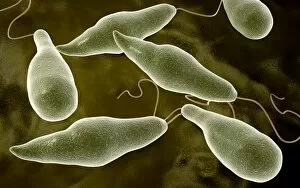
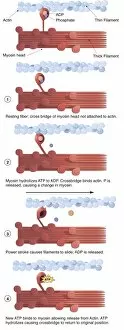
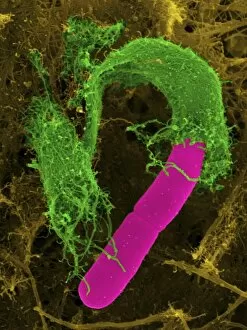
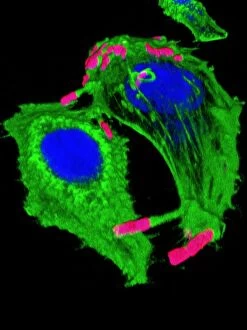
Motility, the driving force behind cellular movement and locomotion, is a captivating phenomenon that unveils the intricate world of cell structure. From the title page of De motu animalium to anatomical details captured in illustrations, this concept has fascinated scientists for centuries. In our quest to understand motility, we delve into the realm of animals and human figures intricately connected by microscopic views of paramecium. These single-celled organisms exhibit astonishing capabilities as they navigate their environment with grace and precision. The illustration of muscle contraction serves as a visual reminder that motility extends beyond unicellular life forms. It showcases how muscles work harmoniously to generate motion in complex organisms like us. Conceptual images depicting Euglena further emphasize the diversity within motile organisms. With its whip-like tail called a flagellum, Euglena propels itself forward through water with remarkable agility. Paramecium takes center stage once again in conceptual imagery, highlighting its unique shape and cilia-covered surface responsible for swift movements. These microscopic views offer glimpses into the mesmerizing world where cells come alive through dynamic motion. As we explore deeper into this captivating subject matter, it becomes evident that motility transcends mere physicality; it represents an essential aspect of life's grand tapestry. Whether observed under a microscope or contemplated conceptually, these images remind us of nature's awe-inspiring ability to create diverse mechanisms for movement at all scales. Motility unravels secrets hidden within cell structures and invites us on an enchanting journey through the wonders of biology, and is a testament to life's incredible adaptability and resilience—a constant reminder that even at our most fundamental level, we are beings driven by motion and exploration.