Compounds Collection (page 9)
"Exploring the Fascinating World of Compounds: From Copper and Magnesium Sulphate to Graphene" Delving into the intricate beauty of compounds
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
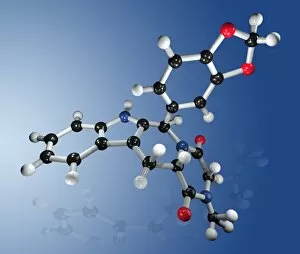
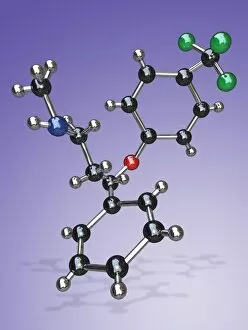
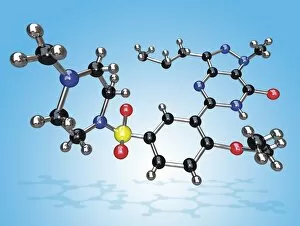
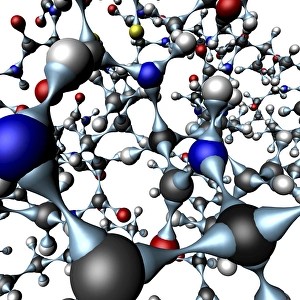
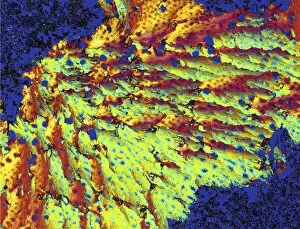
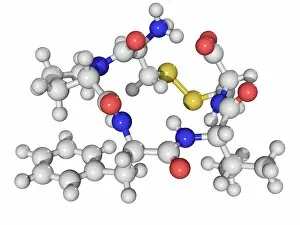
"Exploring the Fascinating World of Compounds: From Copper and Magnesium Sulphate to Graphene" Delving into the intricate beauty of compounds, we witness the mesmerizing sight of copper and magnesium sulphate crystals under a light microscope (LM). A closer look at caffeine crystals through a light micrograph reveals their captivating structure, resembling tiny jewels that fuel our mornings. Oxytocin hormone crystals, captured using polarized light microscopy (PLM C016 / 7196), unveil the remarkable complexity behind this molecule responsible for human bonding. Through an artistic representation, we unravel the secondary structure of proteins – nature's building blocks that orchestrate countless biological processes within us. The perovskite crystal structure captivates scientists with its potential applications in renewable energy technologies, promising a brighter future for sustainable power generation. Another glimpse into oxytocin's world showcases its crystalline form under a light microscope, reminding us of its vital role in nurturing social connections and maternal instincts. Zooming in on caffeine's molecular composition unveils its drug-like qualities that stimulate our nervous system and keep us awake during long nights or early mornings. Peering into the microscopic realm reveals bacterial ribosomes - miniature protein factories essential for life itself - showcasing nature's incredible machinery at work. Cortisol crystals come to life as they are illuminated by a beam of light under a microscope, offering insight into this stress hormone's unique properties within our bodies. Exploring vitamin B12 through its molecular model highlights how this crucial nutrient supports various bodily functions while displaying an elegant arrangement of atoms and bonds. Once again, copper sulphate crystals enchant us with their vibrant colors when observed using a light microscope (LM), reminding us of their diverse industrial uses and chemical significance. Stepping into the realm of materials science brings forth graphene.