Motile Collection
"Exploring the World of Motile Microorganisms: A Captivating Journey" Embark on a mesmerizing journey into the microscopic realm
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
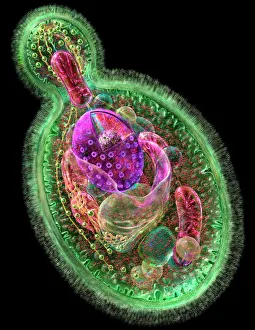
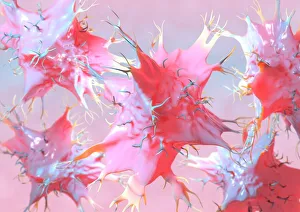
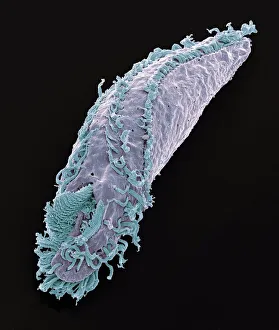
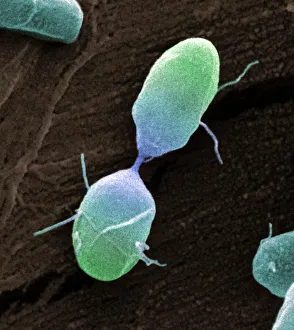
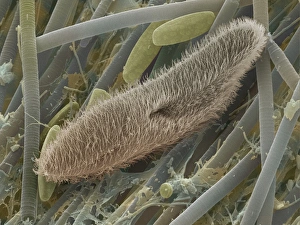
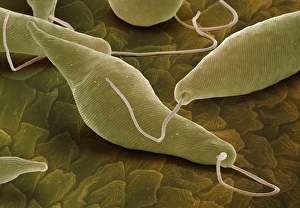
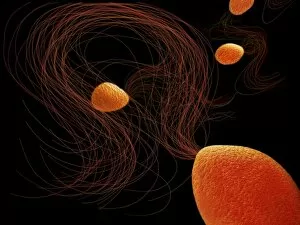
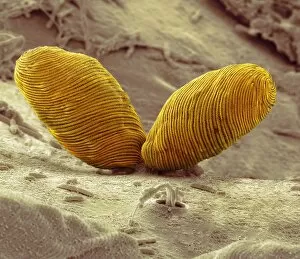
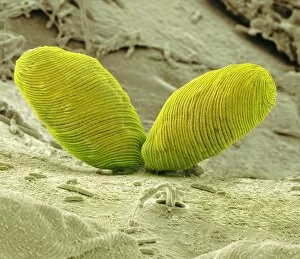
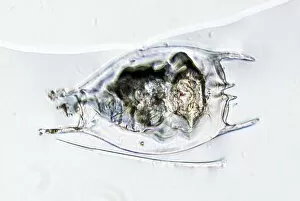
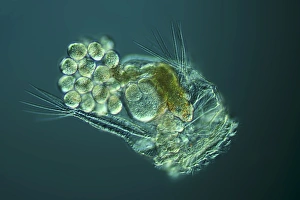
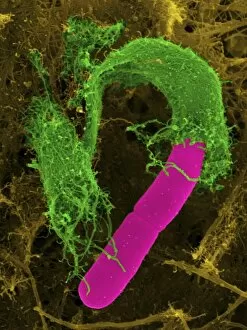
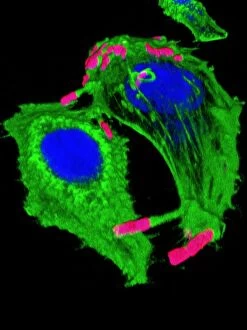
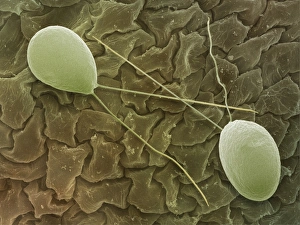
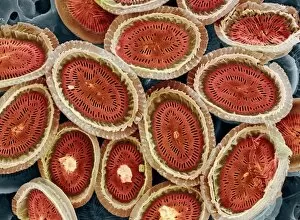
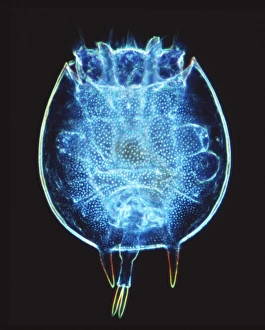
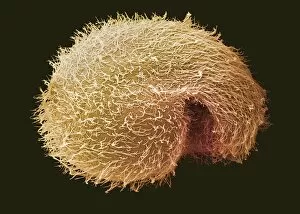
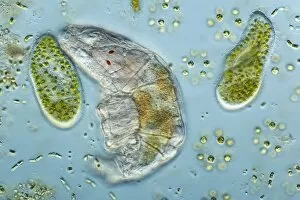
"Exploring the World of Motile Microorganisms: A Captivating Journey" Embark on a mesmerizing journey into the microscopic realm, where life thrives in its most diverse and dynamic forms. From budding yeast cells to dendritic cells, from oxytricha ciliate protozoans to salmonella bacteria dividing, witness the incredible motility that drives these organisms forward. In this captivating artwork depicting dendritic cells, we are reminded of their crucial role in our immune system's defense mechanism. Their ability to move swiftly and efficiently allows them to detect foreign invaders and initiate an immune response. The intricate SEM image of Oxytricha ciliate protozoan showcases its remarkable mobility as it glides through water with grace. Its hair-like structures called cilia propel it forward, enabling it to navigate its surroundings effortlessly. Witness the awe-inspiring sight of a Salmonella bacterium dividing under the scanning electron microscope (SEM). This tiny organism demonstrates its agility as it multiplies rapidly, highlighting its adaptability and survival instincts. Plate 14 Peridinium Peridinea from Kunstformen der Natur by Ernst Haeckel introduces us to another fascinating motile creature. The delicate beauty of this peridinium species is captured in stunning detail, showcasing nature's artistic prowess. Paramecium sp. , another intriguing protozoan species seen through SEM imaging, exhibits swift movements using hair-like projections known as cilia. These tiny creatures gracefully swim through their aquatic habitat while feeding on bacteria and other microorganisms. Euglena gracilis reveals itself under SEM as a single-celled organism equipped with both flagellum for locomotion and chloroplasts for photosynthesis. Its ability to move towards light sources demonstrates nature's ingenious adaptations for survival. Pyrococcus furiosus archaea artwork portrays these heat-loving microorganisms thriving near hydrothermal vents deep beneath the ocean surface. Despite extreme conditions, they exhibit astonishing motility, defying the odds and thriving in their unique environment.