Biomolecule Collection (page 2)
"Biomolecules: Unveiling the Intricate World of Life's Building Blocks" Peering through the lens of scientific discovery
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
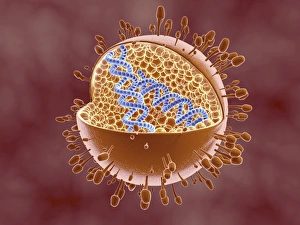
"Biomolecules: Unveiling the Intricate World of Life's Building Blocks" Peering through the lens of scientific discovery, we witness a microscopic view of the human respiratory syncytial virus, unraveling its intricate structure and shedding light on its mechanisms. Zinc fingers delicately embrace a DNA strand, forming an elegant dance between proteins and genetic material. This interaction holds the key to unlocking the mysteries encoded within our genes. The SARS coronavirus protein stands as a formidable foe in our battle against infectious diseases. Understanding its structure is crucial for developing effective treatments and vaccines. Illustrated with precision, a protein takes center stage, showcasing nature's artistic design. Its complex folds and twists hold immense power in shaping life's diverse forms and functions. TFAM transcription factor gracefully binds to DNA C015/7059, orchestrating gene expression like a conductor leading an orchestra. This molecular symphony plays a vital role in maintaining cellular harmony. Stylized rabies virus particles remind us of nature's ability to create both beauty and danger simultaneously. The intricacies hidden within these tiny entities have captivated scientists for centuries. A glimpse into the microscopic world reveals yellow fever virus particles resembling vibrant orbs dancing amidst darkness—a reminder that even invisible threats can wield significant impact on human health. Conceptual imagery portrays the enigmatic rabies virus—an embodiment of fear lurking in shadows yet inspiring relentless pursuit towards understanding this deadly pathogen. MyoD muscle protein-DNA complex showcases how molecules choreograph muscle development—binding together like partners engaged in an exquisite ballet that shapes our physical strength. MscL ion channel protein structure presents itself as nature's gateway—allowing ions to traverse cell membranes with precise control over vital processes essential for life itself. Adenovirus hexon protein emerges as an architectural masterpiece—a structural cornerstone dictating viral entry into host cells while captivating researchers seeking innovative antiviral strategies.