Alpha Helix Collection (page 10)
The alpha helix, a fundamental structure in biology, plays a crucial role in various molecular processes
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
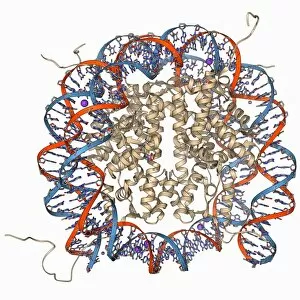
The alpha helix, a fundamental structure in biology, plays a crucial role in various molecular processes. From DNA transcription to protein synthesis, this intricate arrangement is found throughout the biological world. In the realm of genetics, the alpha helix participates in DNA transcription by aiding in the unwinding and separation of strands. Its elegant spiral shape allows for efficient reading and copying of genetic information. When it comes to proteins, the alpha helix serves as a secondary structure that contributes to their stability and function. Visualized through stunning artwork or molecular models, its coiled form adds strength and flexibility to these vital biomolecules. One example where we can observe this remarkable structure is within the nucleosome molecule. Here, DNA wraps around histone proteins forming tight coils resembling beads on a string – with each bead representing an alpha helix. Another instance occurs within bacterial ribosomes responsible for protein synthesis. The presence of multiple alpha helices enables precise positioning of molecules during translation – ensuring accurate assembly of amino acids into functional proteins. Viruses also exploit this structural motif; one such case being HIV reverse transcription enzyme. This enzyme utilizes an alpha helical region to convert viral RNA into DNA – a critical step in viral replication. Similarly, hepatitis C virus enzyme employs an intricate network of alpha helices depicted by molecular models. These structures aid in catalyzing chemical reactions necessary for viral survival and proliferation. Moving beyond viruses, manganese superoxide dismutase enzyme showcases how nature harnesses the power of the alpha helix for antioxidant defense mechanisms within cells. Its tightly wound coils protect against harmful free radicals that can damage cellular components. Alpha-helical motifs are not limited to enzymes alone but extend to larger molecules like human serum albumin or Argonaute protein involved in gene regulation pathways. Their well-defined arrangements contribute significantly to their respective functions within our bodies' complex systems.