Geodesy Collection
Geodesy, the science of measuring and understanding Earth's shape and gravitational field, has fascinated minds throughout history
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
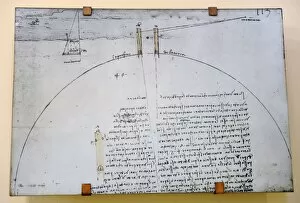
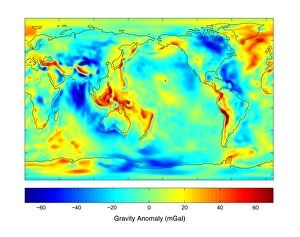
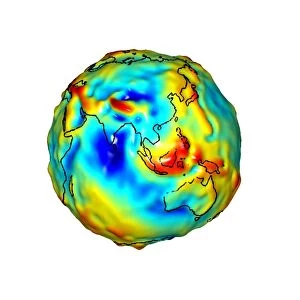
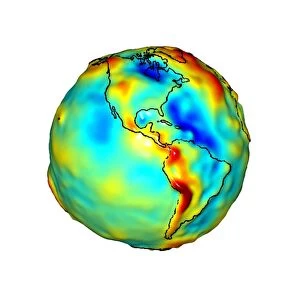
Geodesy, the science of measuring and understanding Earth's shape and gravitational field, has fascinated minds throughout history. From Leonardo da Vinci to Carlos Ibanez de Ibero, brilliant individuals have contributed to our knowledge of this vast subject. Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519), a true Renaissance genius, pondered over the circumference of the Earth. His curiosity led him to explore various aspects of geodesy, leaving behind invaluable insights for future generations. Carlos Ibanez i Ibanez de Ibero, Marquis of Mulhacen (1825-1890), further expanded on geodesy with his meticulous engravings. Through his detailed artwork, he captured the essence and complexity of this scientific discipline. Gravity maps play a crucial role in geodesy as they reveal variations in Earth's gravitational field. The colorful gravity maps C018/9377, C018/9376, and C018/9374 provide valuable information about our planet's composition and structure. Gills Egypt baseline survey conducted in 1875 is another remarkable milestone in geodesy. This survey laid down precise measurements that formed the foundation for modern mapping techniques still used today. Felix Vening Meinesz was a Dutch geophysicist who made significant contributions to geodesy. His work revolutionized underwater gravity measurements using innovative instruments like theodolites and astronomical instruments. Geodesy encompasses an array of fascinating tools such as theodolites - precise optical instruments used for measuring angles between visible points. These devices have been instrumental in accurately determining distances on land or at sea. As we delve into the world of geodesy, we uncover not only facts about our planet but also marvel at humanity's relentless pursuit of knowledge, and is through these endeavors that we gain a deeper understanding of Earth's mysteries while appreciating its immense beauty from every angle imaginable.