Central Nervous System Collection (page 9)
The central nervous system, the intricate network that governs our every thought and movement, is a marvel of complexity
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
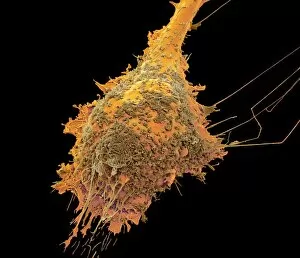
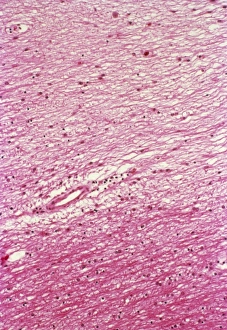
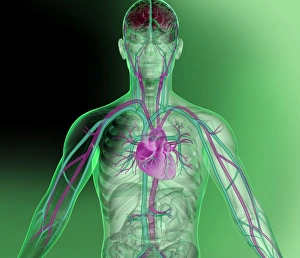
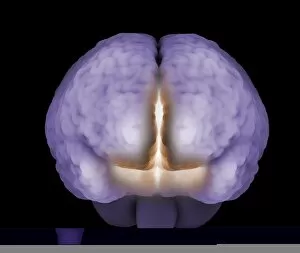
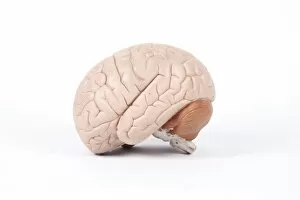
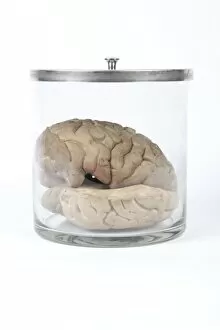
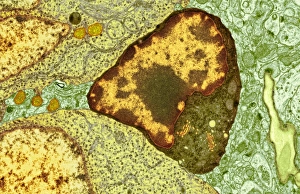
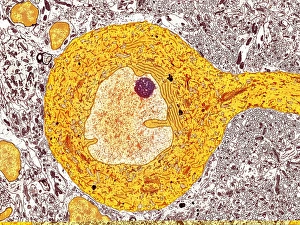
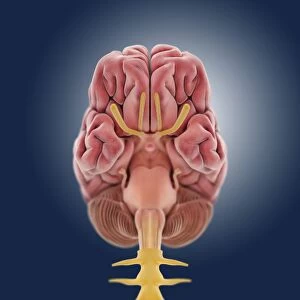
The central nervous system, the intricate network that governs our every thought and movement, is a marvel of complexity. From the delicate cerebellum tissue to the detailed light micrograph capturing its essence, we are reminded of its importance in maintaining balance and coordination. Anatomy comes alive as we explore the human brain from an inferior view. The intricacy of brain fibers is revealed through DTI MRI scans like C017/7099 and C017/7035, showcasing their vital role in transmitting information throughout this extraordinary organ. Artistic renderings bring us closer to understanding the medulla oblongata's significance within the brain. Its portrayal in various artworks allows us to appreciate how it controls essential functions such as breathing and heart rate. As we delve deeper into studying the central nervous system, models of the human brain provide invaluable insights into its structure and organization. Lateral views reveal countless regions responsible for cognition, emotion regulation, sensory perception, and motor control. Microscope slides offer glimpses into nerve cells' intricate architecture—a testament to their ability to transmit electrical signals at lightning speed. Meanwhile, glial stem cell cultures captured under a light microscope remind us of their crucial role in supporting neuronal function. Finally, artistic representations unveil the limbic system's enigmatic nature—an interconnected web responsible for emotions and memory formation. These captivating artworks allow us to visualize this complex network within our brains. Exploring these hints provides a glimpse into the awe-inspiring world of our central nervous system—the very foundation upon which our thoughts, actions, memories reside—reminding us just how remarkable our brains truly are.