Cell Wall Collection
The cell wall, a remarkable structure found in various organisms, plays a crucial role in providing support and protection
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
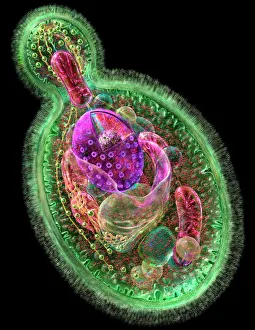
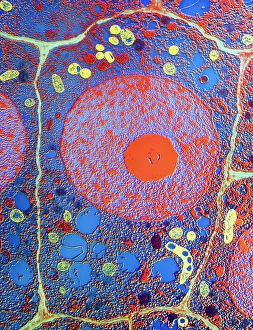
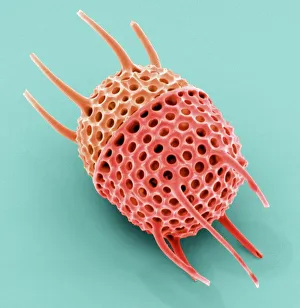
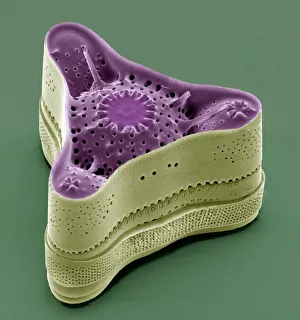
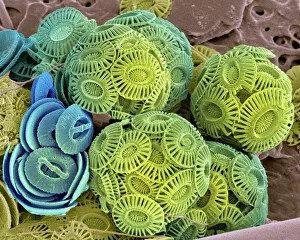
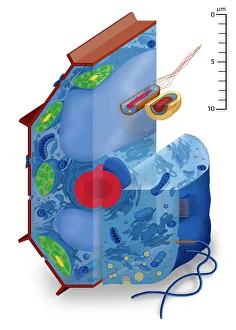
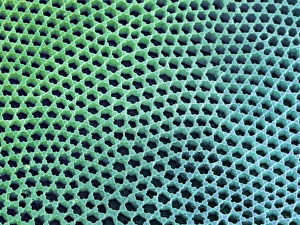
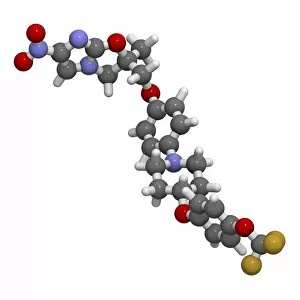
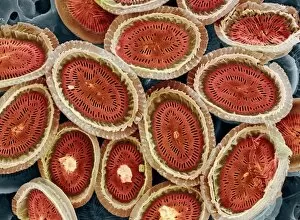
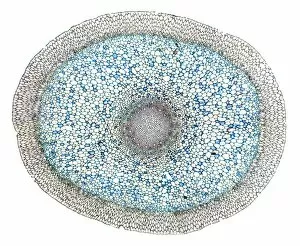
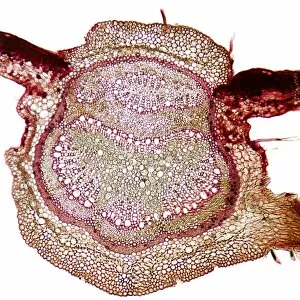
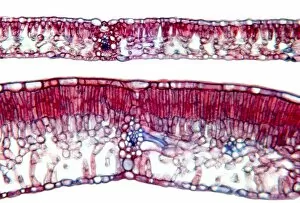
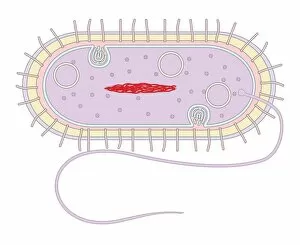
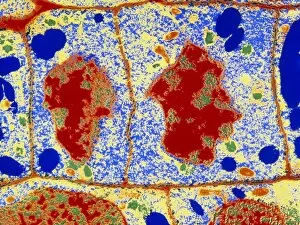
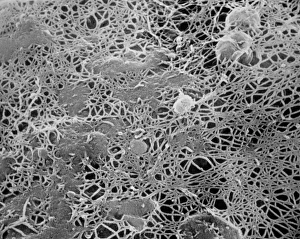
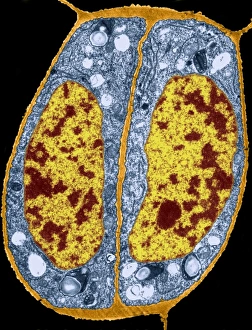
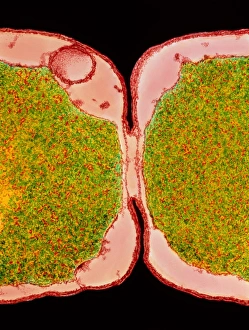
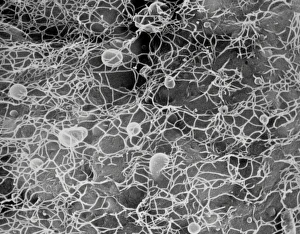
The cell wall, a remarkable structure found in various organisms, plays a crucial role in providing support and protection. From budding yeast cells to calcareous phytoplankton and diatoms, the diversity of cell walls is awe-inspiring. Under the scanning electron microscope (SEM), we can observe the intricate details of these fascinating structures. The budding yeast cell showcases its robust cell wall, which not only maintains its shape but also defends against external threats. Moving on to calcareous phytoplankton, their SEM image reveals an intricately patterned cell wall that helps them thrive in aquatic environments. These delicate organisms rely on their sturdy armor-like walls for buoyancy and protection from predators. Diatoms, another group of microorganisms with stunningly beautiful glass-like shells visible through SEM imaging, exhibit an astonishing array of shapes and patterns. Their intricate designs are not just visually captivating but also serve as effective barriers against environmental stressors. Artwork depicting different types of cells highlights the diverse nature of cell walls across various species. Each artwork represents unique characteristics specific to each organism's needs for survival and adaptation. Zooming in further under SEM magnification, we witness the mesmerizing complexity of diatom cell walls. These microscopic wonders showcase an unparalleled level of precision in their geometric arrangements—a testament to nature's ingenuity at work. Not limited to single-celled organisms alone, plant cells also possess formidable cellulose-based walls that provide structural integrity while allowing flexibility for growth and development. In this series of SEM images capturing diatoms' incredible beauty up close—each frame showcasing distinct shapes—we are reminded once again how vital these structures are for these tiny creatures' existence amidst vast oceans or freshwater bodies worldwide. From simple yet resilient budding yeast cells to elaborate calcareous phytoplankton and breathtakingly intricate diatoms—their varied forms highlight the versatility and importance of cellular architecture known as the cell wall.