Pseudopod Collection
"Pseudopods: The Dynamic Extensions of Life's Microscopic World" In the vast realm of microscopic wonders
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
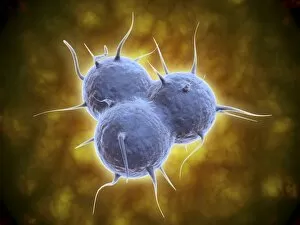
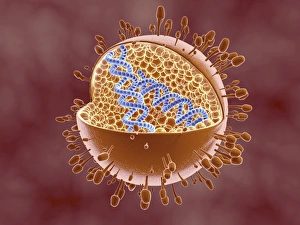
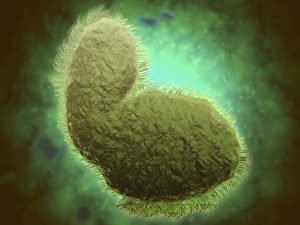
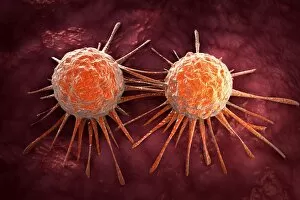
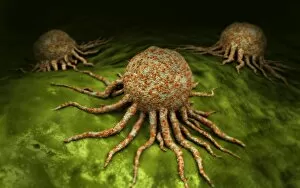
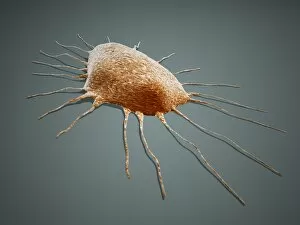
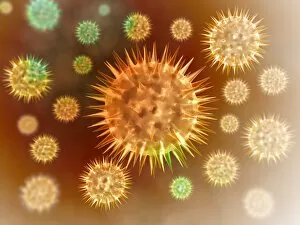
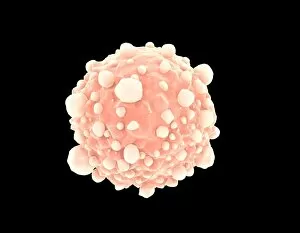
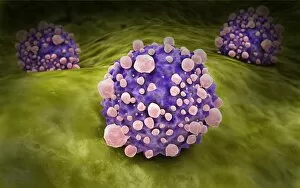
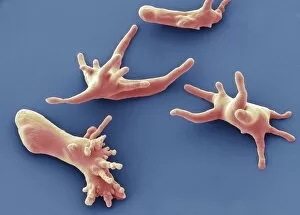
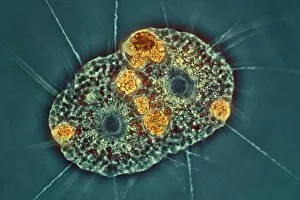
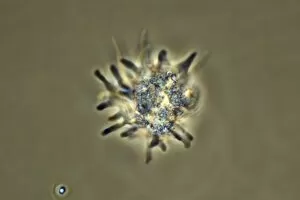
"Pseudopods: The Dynamic Extensions of Life's Microscopic World" In the vast realm of microscopic wonders, pseudopods stand as remarkable extensions that shape and define life. These fascinating protrusions are seen in various forms, each with its own unique purpose. From the microscopic view of human respiratory syncytial virus, we witness how these tiny organisms utilize pseudopods to infiltrate our respiratory system, causing infections and illnesses. Similarly, an illustration showcasing an amoeba's movement reveals liquid cytoplasm flowing through pseudopods, carrying essential organelles along their path, and is through this mechanism that amoebas navigate their surroundings and seek sustenance. Conceptual images further highlight the significance of pseudopods in different contexts. Radiolarians exhibit intricate skeletal frames supported by delicate pseudopodial extensions, enabling them to capture prey and thrive within aquatic ecosystems. Meanwhile, cancer cells send out pseudopods in the direction of motion while red blood cells flow nearby—a visual representation of cancer's invasive nature within our bodies. Delving into viral replication processes unveils another facet where pseudopodia play a crucial role. RNA viruses replicate themselves with astounding efficiency using these dynamic projections as they invade host cells' DNA structures—depicted through a cutaway view of Reoviridae virus revealing its genetic material inside. The impact on human health becomes evident when examining pancreatic cancer cells under a microscope—an affliction characterized by abnormal cell growth and migration facilitated by malignant pseudo-extensions. Conceptual images depicting cancer viruses emphasize their ability to exploit cellular mechanisms via deceptive pseudo-appendages for survival and proliferation. Pseudopods encapsulate both wonderment and concern within life's infinitesimal dimensions. They serve as conduits for pathogens but also enable vital functions necessary for survival. Understanding these versatile extensions unravels mysteries hidden from plain sight—a testament to the intricacies present even at microscopic levels.