Astrolabe Collection
The astrolabe, a remarkable instrument used for centuries to navigate the celestial bodies, has played a significant role in the history of astronomy
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
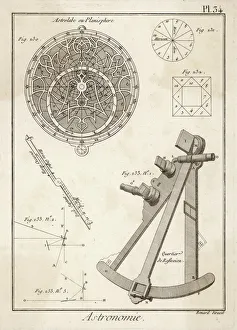
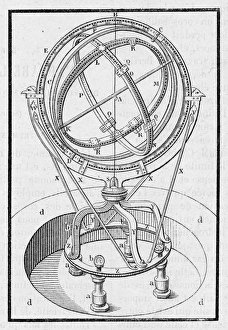
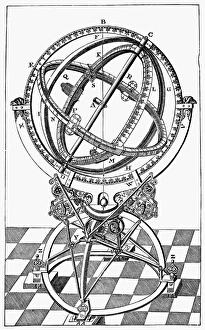
The astrolabe, a remarkable instrument used for centuries to navigate the celestial bodies, has played a significant role in the history of astronomy. Developed alongside the quadrant, it allowed astronomers like Tycho Brahe to make precise measurements and observations. One notable example is the astrolabe created by German mathematician and astronomer Johann Müller, also known as Regiomontanus. This 15th-century masterpiece showcased his expertise in both mathematics and astronomy. Turkish astronomers in Istanbul also utilized the astrolabe extensively during their studies. Ottoman manuscript illuminations from the late 16th century depict these scholars using this instrument within their observatory. D'Urville's astrolabe stands as an old but crucial tool that enabled sailors to roughly mark celestial positions before sextants were invented. Its line engraving showcases its significance in maritime navigation. Tycho Brahe, a Danish astronomer renowned for his accurate astronomical observations, relied heavily on his nautical astrolabe from Spain in 1571. This device aided him greatly in mapping out stars and planets with precision. Another variant of this incredible invention is seen through an astronomical astrolabe dating back to 1598. Its intricate design demonstrates how advancements were made over time to enhance accuracy and functionality. Astronomy enthusiasts may recognize the Prague Astronomical Clock or Prague Orloj as one of Europe's most famous an astronomicastolrable clock tower. It not only tells time but also displays various astronomical details such as planetary positions and phases of the moon. From its origins in the 15th century to its continued use well into the 19th century, including even until around 1870 when Angel Apostles adorned some versions; allegorical depictions often accompanied this fascinating instrument throughout history.