Semicircular Canal Collection
The semicircular canal, a vital component of the human ear, has been intricately studied and illustrated throughout history
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
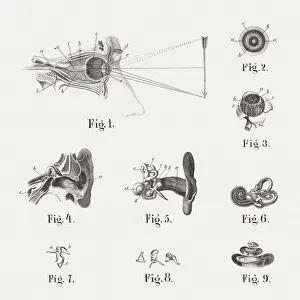
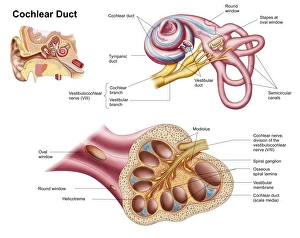
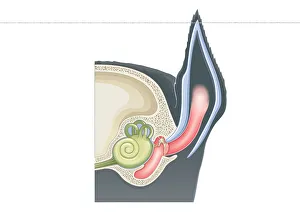
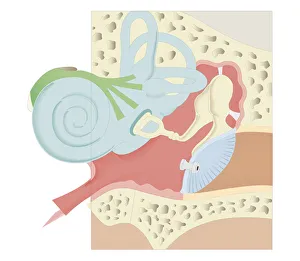
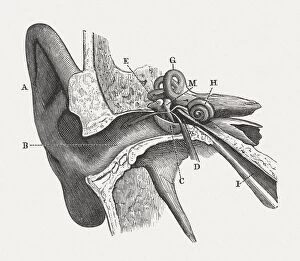
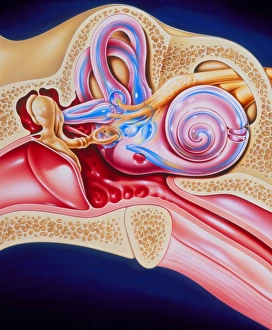
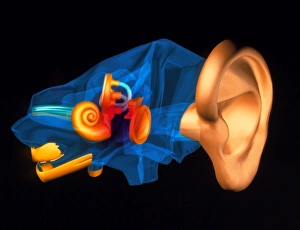
The semicircular canal, a vital component of the human ear, has been intricately studied and illustrated throughout history. In an anatomy publication from 1861, the semicircular canal was highlighted alongside other eye and ear structures. Its significance in auditory function is further emphasized in a digital cross-section illustration of the mammalian ear, showcasing its position amidst the pinna, eardrum, and middle ear. Not limited to humans alone, a cross-section illustration of a domestic cat's ear also features the semicircular canal as an essential part of their auditory system. Biomedical illustrations provide detailed insights into this intricate structure within our own ears as well. From cross-sectional views to internal components depicted with precision, these illustrations offer valuable knowledge about its role in maintaining balance and spatial orientation. Furthermore, biomedical illustrations showcase various procedures related to the semicircular canal. One such depiction reveals a grommet inserted into the eardrum for medical purposes while another illustrates tympanometry - a test conducted using a probe inserted into the ear to assess both middle ear functionality and eardrum health. Delving deeper into its complexity, interior details of the cochlea are also explored through biomedical illustrations. This spiral-shaped structure houses sensory cells responsible for converting sound vibrations into electrical signals that our brain can interpret. Numerous biomedical illustrations have shed light on different aspects of the semicircular canal's anatomy over time.