Microvillus Collection
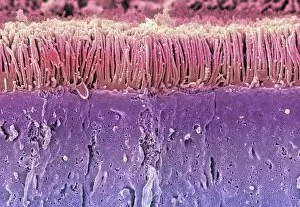
Microvilli are tiny, finger-like projections that cover various surfaces in our body, playing crucial roles in different physiological processes
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
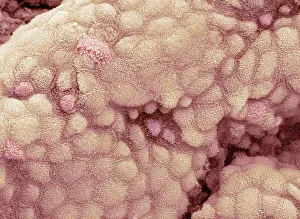
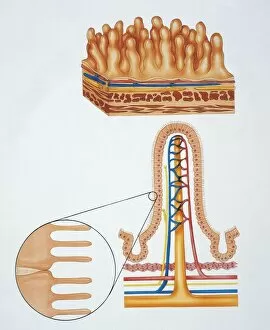
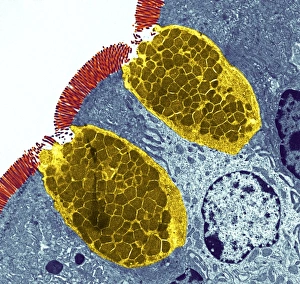
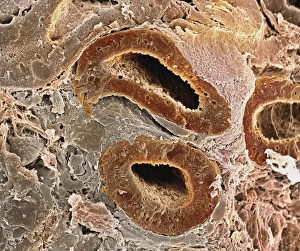
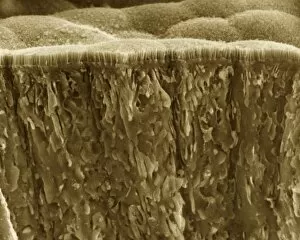
Microvilli are tiny, finger-like projections that cover various surfaces in our body, playing crucial roles in different physiological processes. When examining the gallbladder surface under a scanning electron microscope (SEM), these microvilli appear as numerous small protrusions, enhancing the organ's ability to absorb nutrients efficiently. An illustration depicting intestinal villi showcases the intricate structure of microvilli found on their surface. These microscopic folds increase the absorptive area of the intestines, aiding in nutrient absorption and digestion. Under a transmission electron microscope (TEM), we can observe intestinal microvilli up close. These delicate structures extend from the epithelial cells lining our intestines and further amplify nutrient absorption by maximizing contact with digested food particles. In another fascinating view inside our bodies, a microscopic image reveals white blood cells navigating through blood vessels. Here, microvilli within these vessels contribute to maintaining proper blood flow and facilitating immune responses when encountering pathogens or injuries. Venturing into the auditory system, an interior detail of the cochlea unveils specialized hair cells adorned with microvilli. These sensory structures convert sound vibrations into electrical signals for us to perceive sounds accurately. Examining red blood cells alongside leukocytes provides insight into how microvillous interactions occur within our circulatory system. Microvilli on endothelial cells lining arteries help regulate blood flow while allowing efficient exchange between oxygen-carrying red blood cells and protective white blood cells defending against infections. During embryonic development, blastomeres cluster together forming a developing morula – an early stage embryo consisting of multiple dividing cells. Microscopic examination highlights how cell-to-cell communication facilitated by intercellular bridges formed by microvilli plays a vital role in this process. Zooming back into circulation dynamics, observing red blood cell flow inside an artery demonstrates how smoothly they navigate past each other thanks to well-organized arrangements of endothelial cell microvilli along vessel walls.