Insulating Collection
Insulating is a fascinating process that can be observed in various aspects of our world
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
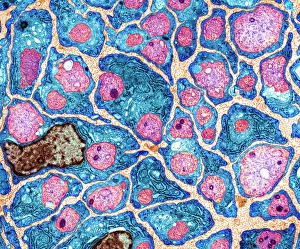
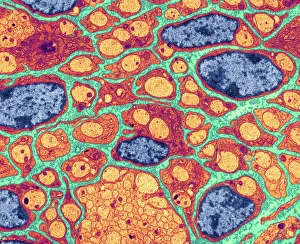
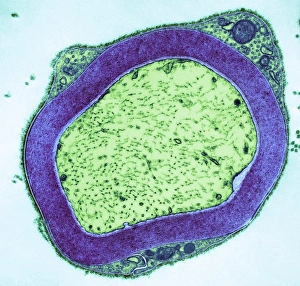
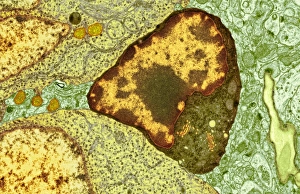
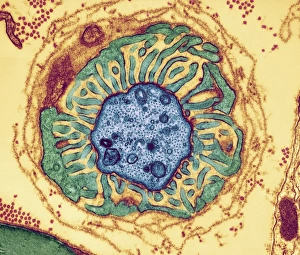
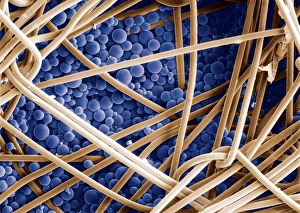
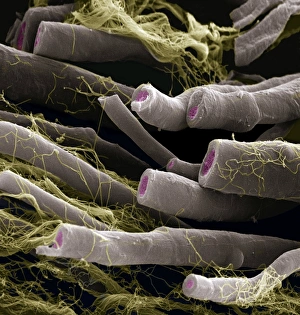
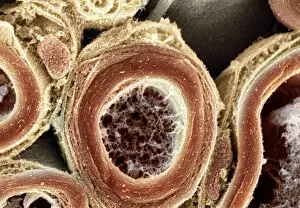
Insulating is a fascinating process that can be observed in various aspects of our world. One example is the myelination of nerve fibers, which can be visualized using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). This intricate process involves the formation of a protective layer around nerve fibers, enhancing their efficiency and speed. Another instance of insulation can be found in hot water cylinders with jackets. These jackets act as thermal barriers, preventing heat loss and ensuring that the water stays warm for longer periods. It's amazing how such a simple addition can significantly improve energy conservation. In the realm of scientific exploration, we come across Jean Jallabert investigating the effects of points and knobs on electrical discharges. Through his experiments, he aimed to understand how different shapes could influence electrical flow and potentially enhance insulation properties. The Casellis pantelegraph also played a role in communication insulation. At the sending station, dispatches were written or drawn on this device before being transmitted electronically. This invention revolutionized long-distance communication by providing an insulated means to transmit information. William Watson's glass-globe electrical machine was another breakthrough in insulating technology during its time. Generating charges within its glass globe enclosure allowed for controlled electricity production while minimizing potential hazards. Furthermore, experiments have been conducted to ascertain the effects of electricity on water under high voltage conditions. These investigations help us understand how materials behave when exposed to extreme electric fields and aid in developing better insulators for various applications. Nature itself provides effective insulation methods too. The polar bear's insulating hair plays a crucial role in keeping it warm even in freezing temperatures. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images reveal the intricate structure responsible for trapping air pockets that act as excellent thermal insulators. Additionally, polar bears possess underhair that further enhances their ability to withstand harsh cold environments by providing additional layers of protection against temperature fluctuations - yet another remarkable adaptation. Lastly, modern-day comforts like electric blankets utilize heating elements that are carefully designed and insulated to ensure safety and efficiency.