Fluorescence Collection (page 3)
"Unveiling the Vibrant World of Fluorescence
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
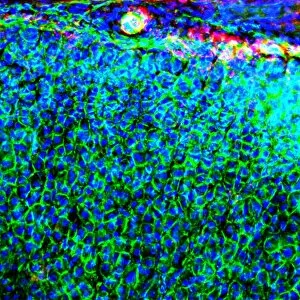
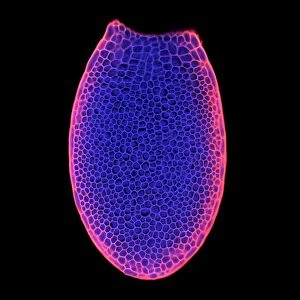
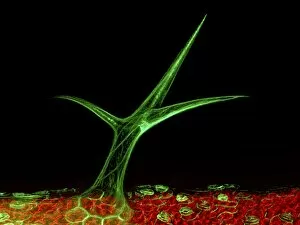
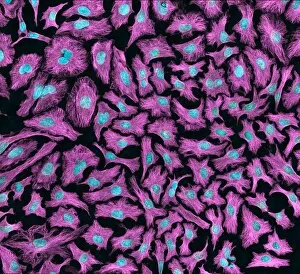
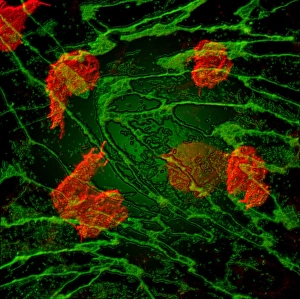
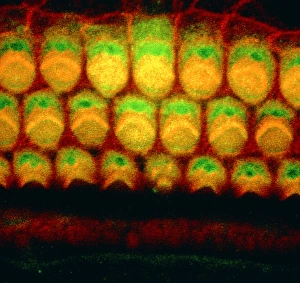
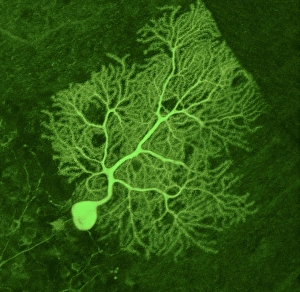
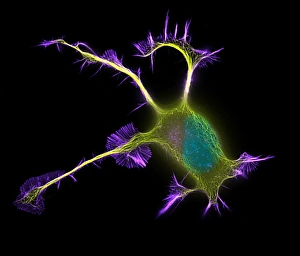
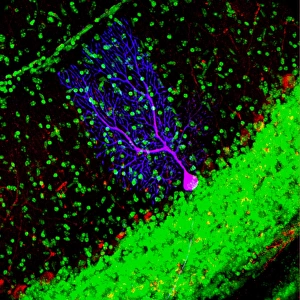
"Unveiling the Vibrant World of Fluorescence: Illuminating Cerebellum Tissue and Nerve Cells" Exploring the intricate beauty of cerebellum tissue through a mesmerizing light micrograph. Dive into the microscopic realm as nerve and glial cells come to life in a captivating light micrograph. Unraveling the secrets of glial cells with stunning clarity, thanks to a confocal light micrograph. Witness the enchanting glow of HeLa cells under a powerful microscope - an awe-inspiring sight captured in C017 / 8299. Delving deep into cell structure, fluorescence reveals hidden wonders that are otherwise invisible to our naked eyes. Marvel at the ethereal radiance emitted by HeLa cells, portrayed beautifully in C017 / 8298 - an image worth cherishing. Embark on a visual journey through cerebral cortex nerve cells, where fluorescence paints a vivid picture of their interconnectedness. Witness nature's miracle unfold as cell division is brought to life through an enchanting fluorescent micrograph. Behold another breathtaking view of cerebellum tissue illuminated by vibrant fluorescence - showcasing its complexity and elegance once again. Reflecting on history, discover how even X-ray security machines from 1900 were early pioneers in harnessing fluorescence for enhanced safety measures during screenings. Fluorescence unveils hidden worlds within ourselves and beyond – from delicate tissues to cellular processes – reminding us that there is always more than meets the eye.