Flowering Part Collection (page 3)
"Exploring the Intricate Beauty of Flowering Parts
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
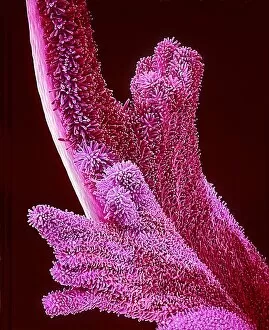
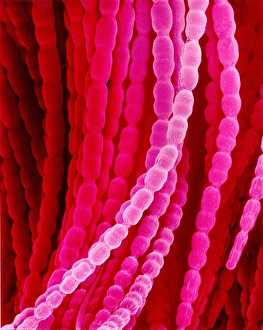
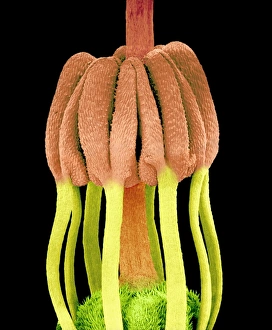
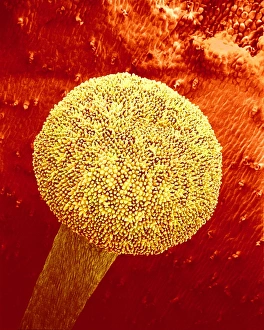
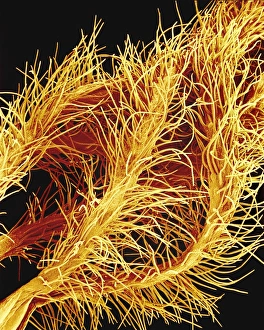
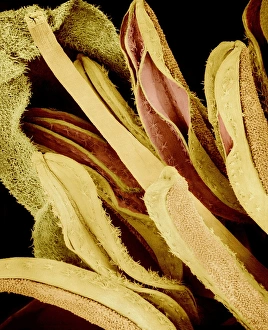
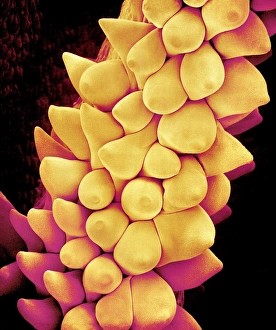
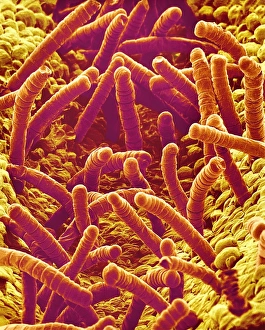
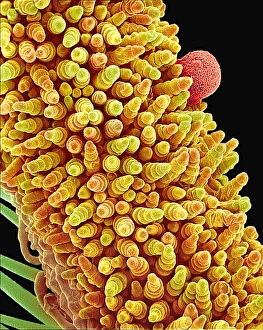
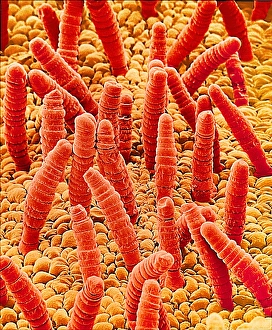
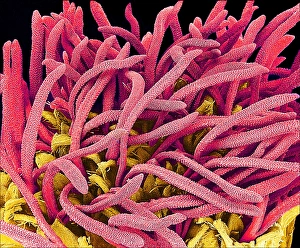
"Exploring the Intricate Beauty of Flowering Parts: A Captivating SEM Journey" Delve into the mesmerizing world of flowering parts as we embark on a captivating scanning electron microscope (SEM) adventure. Witness the intricate details and stunning structures that make up these botanical wonders. The Easter cactus stigma, magnified through SEM, reveals its delicate and feathery texture, showcasing nature's artistry at its finest. The Tea flower stamens come alive under the microscope, displaying their vibrant colors and fascinating patterns that attract pollinators with precision. A closer look at the Buttercup flower exposes its velvety petals in exquisite detail. Each petal seems to dance with light, inviting us to appreciate its ephemeral beauty. Meanwhile, the humble Chickweed flower surprises us with an unexpected burst of color when viewed through false-color SEM imaging techniques. Discovering hidden secrets within flowers continues as we observe oil glands on peppermint petals glistening like tiny droplets of gold. The Aubergine flower petal captivates our senses with its unique shape and intricate surface patterns revealed by SEM technology. Lily petals unfold before our eyes in breathtaking clarity under SEM examination; their graceful curves and delicate veins become works of art themselves. Columbine flower stamens reveal their complex arrangement, designed to ensure successful reproduction for this remarkable species. Diving deeper into nature's marvels, a false-color SEM image unveils the enchanting intricacies of a chickweed flower – each component playing a vital role in attracting pollinators while ensuring survival for generations to come. Yarrow's petal surface becomes an abstract masterpiece when observed through an electron microscope lens - every ridge and groove telling tales of resilience against harsh environments. And finally, witness the ovary of Opium poppy in astonishing detail; this microscopic view offers insights into how life begins within these magnificent blooms.