Eustachian Tube Collection
The Eustachian Tube: A Gateway to Balanced Hearing The intricate workings of the human ear never cease to amaze
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
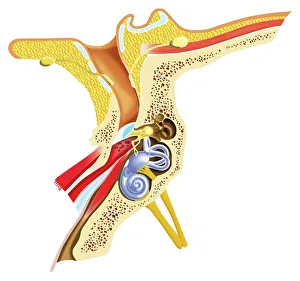
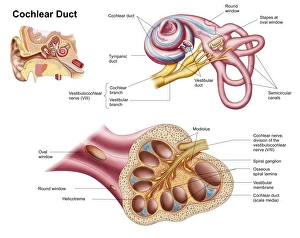
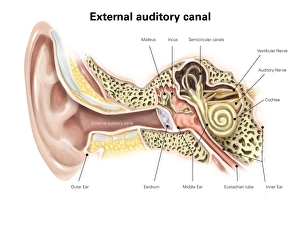
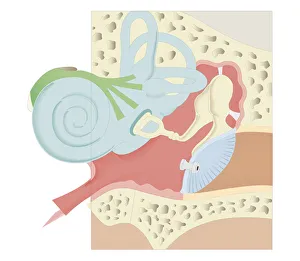
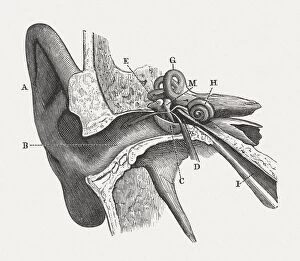
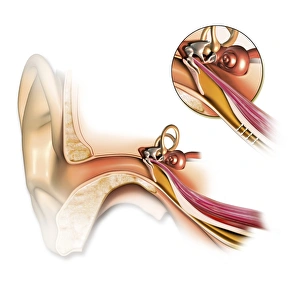
The Eustachian Tube: A Gateway to Balanced Hearing The intricate workings of the human ear never cease to amaze. Among its many remarkable components, the Eustachian tube plays a vital role in maintaining equilibrium and ensuring optimal auditory function. This slender passageway connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx, acting as a crucial link between our hearing apparatus and respiratory system. When we observe a diagram of the inner ear, we can trace this essential conduit alongside other key structures such as the auditory canal, eardrum, semicircular canals, cochlea nerve, and cochlea itself. Its location becomes even more apparent when examining an anatomy illustration highlighting the external auditory canal with labels or a cutaway diagram showcasing various layers within. While humans possess this remarkable feature, it is worth noting that animals like domestic cats also have their own version of this mechanism. A cross-section biomedical illustration reveals how feline ears share similarities with ours but retain unique characteristics specific to their species. Understanding how our bodies adapt is further exemplified by studying cross-sectional biomedical illustrations depicting grommets inserted into eardrums (tympanic membranes). These tiny devices help regulate pressure imbalances within the middle ear and alleviate conditions such as otitis media. Delving deeper into these internal components unveils yet another mesmerizing aspect of our auditory system. Cross-sectional biomedical illustrations provide invaluable insights into not only anatomical structures but also physiological processes occurring within them. By exploring these detailed depictions, we gain a profound appreciation for how each element contributes harmoniously towards our ability to hear sound accurately. Ultimately, comprehending every facet of this complex network allows us to appreciate just how miraculous our sense of hearing truly is. The Eustachian tube serves as both guardian and facilitator—balancing pressures between environments while enabling sound waves to reach their destination unimpeded.