Enzymes Collection
Enzymes: The Tiny Powerhouses of Life From the intricate Glutamine synthetase enzyme to the mesmerizing Lysozome protein crystals, enzymes never cease to amaze us
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
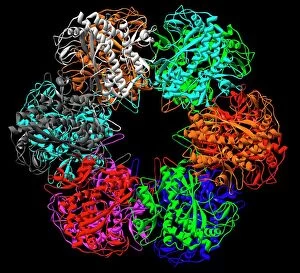
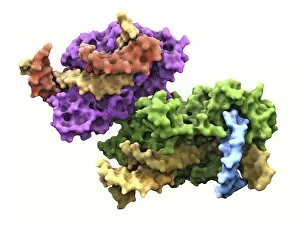
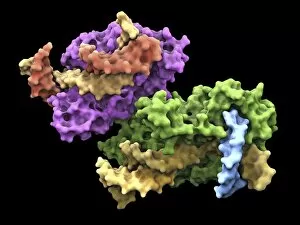
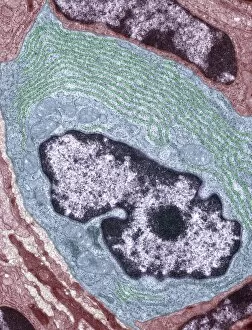
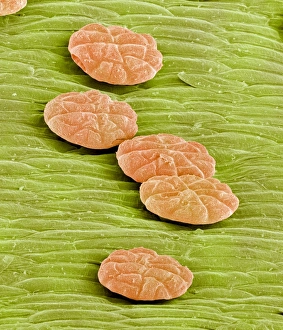
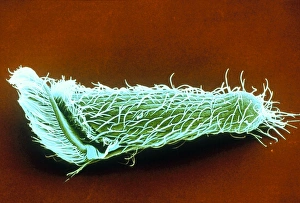
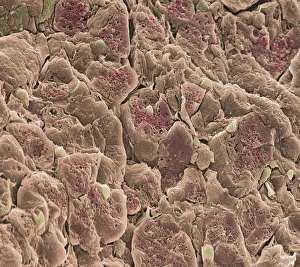
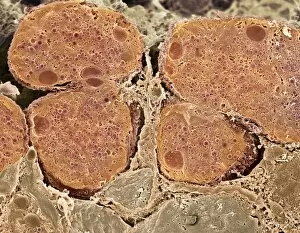
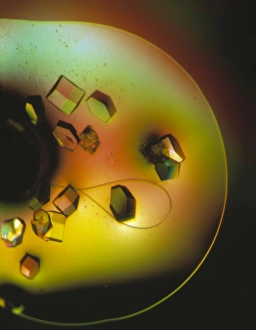
Enzymes: The Tiny Powerhouses of Life From the intricate Glutamine synthetase enzyme to the mesmerizing Lysozome protein crystals, enzymes never cease to amaze us. With X-ray crystallography C016 / 3824 revealing their hidden structures, we uncover a world of complexity and beauty. The Flap endonuclease proteins F007/9914 and F007/9916 play crucial roles in DNA repair, ensuring our genetic material remains intact. Meanwhile, the Ubiquitin activating enzyme protein E1 F007/9908 orchestrates cellular processes by tagging proteins for degradation or modification. Underneath the microscope's lens, Pancreatic exocrine cells reveal their secretory nature while Eosinophil white blood cells stand as guardians against foreign invaders. In this microscopic realm, Pancreatic acinar cells shine with their ability to produce digestive enzymes essential for nutrient breakdown. Through TEM images, we witness the bustling activity within these pancreatic acinar cells as they tirelessly fulfill their vital functions. And let's not forget about those resilient Eosinophil white blood cells that defend our bodies from harm and can truly remarkable entities that drive countless biochemical reactions necessary for life itself. Their diverse structures and functions make them indispensable players in maintaining homeostasis and sustaining living organisms. So next time you marvel at an enzymatic reaction or delve into the fascinating world of molecular biology, remember that behind every biological process lies an army working diligently to keep everything running smoothly.