Ciliated Collection
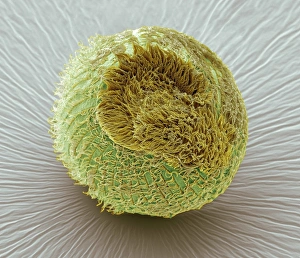
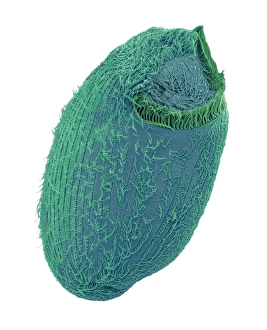
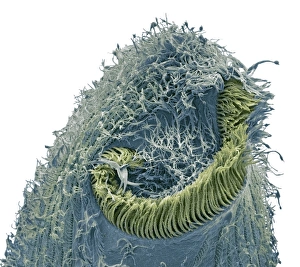
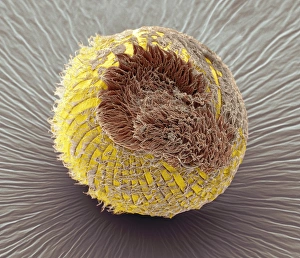
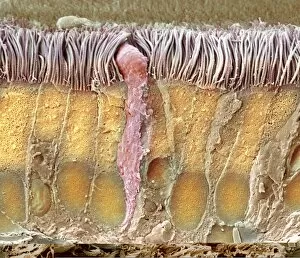
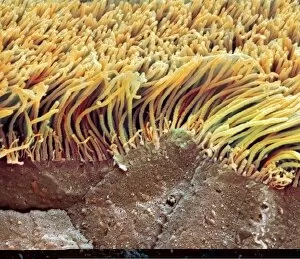
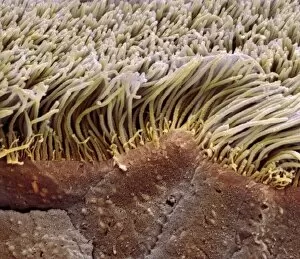
"Ciliated: The Tiny Hair-Like Structures That Power Our Respiratory System" The trachea lining, as observed under a scanning electron microscope (SEM
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
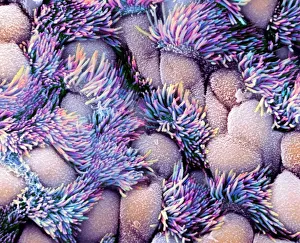
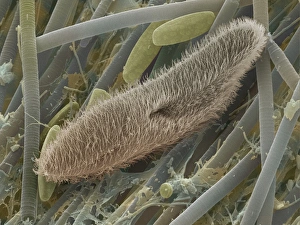
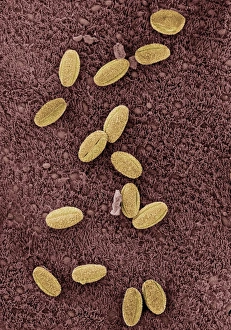
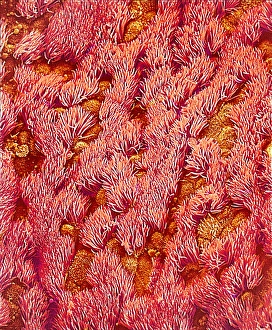
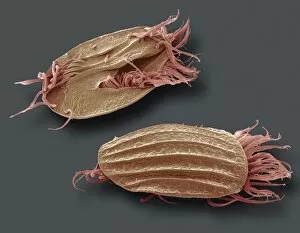
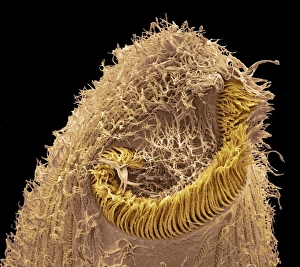
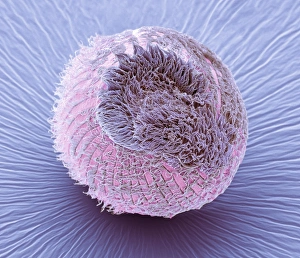
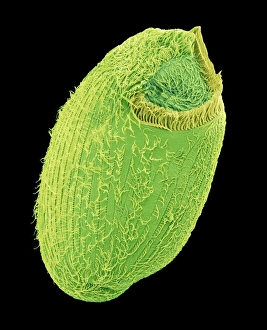
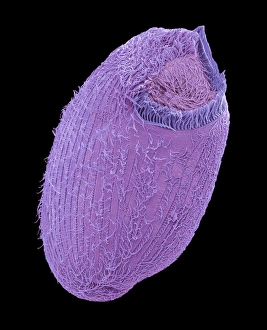
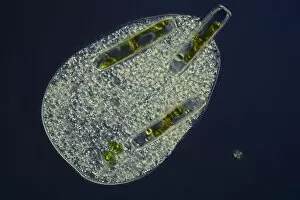
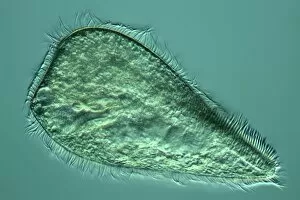
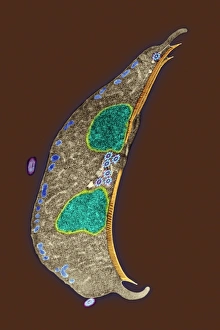
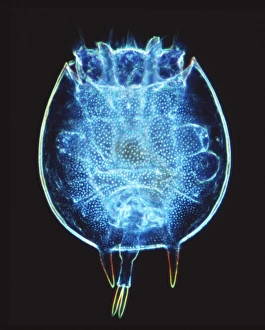
"Ciliated: The Tiny Hair-Like Structures That Power Our Respiratory System" The trachea lining, as observed under a scanning electron microscope (SEM), reveals the intricate network of cilia that play a vital role in our respiratory health. These tiny hair-like structures are responsible for sweeping away mucus and foreign particles from our airways, ensuring smooth breathing. In nature, the canary creeper (Tropaeolum peregrinum) showcases its own ciliated wonders. Delicate tendrils adorned with vibrant flowers exhibit cilia-like projections that aid in climbing and capturing sunlight for photosynthesis. Venturing into the depths of the ocean, we encounter the mesmerizing Crown Jellyfish (Cephea cephea) off the coast of Hawaii, USA. Its translucent body is adorned with countless cilia that propel it gracefully through water while also assisting in feeding by capturing prey. Zooming back to microscopic lifeforms, we discover Paramecium sp. , a fascinating protozoan species. SEM images reveal its densely covered surface with numerous cilia acting as oars to navigate through water environments efficiently. Returning to human anatomy, SEM captures another glimpse of nasal lining where ciliated cells diligently work together to filter out impurities and protect our delicate respiratory system from harmful substances present in the air we breathe. Further exploring the trachea lining using SEM technology (specifically C013 / 7126 and C013 / 7122), we witness these remarkable hair-like structures extending like an army ready to defend against allergens or irritants that may enter our airways. Indeed, these incredible ciliary mechanisms within our trachea serve as guardians against potential harm. Their synchronized movements create a wave-like motion known as mucociliary clearance - an essential defense mechanism protecting us from infections and maintaining healthy lungs. As we delve deeper into microscopy studies, Paramecium sp. Once again captivates our attention.