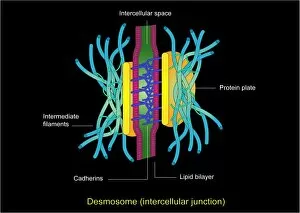
Cellular Collection (page 3)
"Unveiling the Intricacies of Cellular Life: A Journey Through Micrographs" Budding yeast cell: Witness the birth of new life as a budding yeast cell emerges
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
"Unveiling the Intricacies of Cellular Life: A Journey Through Micrographs" Budding yeast cell: Witness the birth of new life as a budding yeast cell emerges, paving the way for future generations. Nerve and glial cells, light micrograph: Delve into the intricate network of nerve and glial cells that form the foundation of our nervous system. Dicotyledon plant stem, light micrograph: Explore the vibrant world within a dicotyledon plant stem, where cells work tirelessly to support growth and development. Rough endoplasmic reticulum, TEM: Peer into the fascinating realm of rough endoplasmic reticulum through a transmission electron microscope (TEM), revealing its role in protein synthesis. Dendritic cells, artwork: Marvel at an artistic representation showcasing dendritic cells' unique shape and function in immune responses. Cell structure: Uncover the hidden beauty within cellular structures as we unravel their complexity and significance in various biological processes. Mitosis, light micrograph: Observe nature's remarkable spectacle – mitosis – captured under a light microscope; witness how one cell divides into two with precision and grace. Cell division, fluorescent micrograph: Immerse yourself in a mesmerizing display of fluorescent colors capturing another facet of cell division's captivating dance. Dohle bodies in blood cell, micrograph: Discover peculiar "Dohle bodies" within blood cells through high-resolution microscopy—a clue to certain health conditions requiring further investigation. Acute promyelocytic leukemia, micrograph : Gain insight into acute promyelocytic leukemia by examining abnormal cellular characteristics observed under powerful magnification—an invaluable tool for diagnosis and treatment strategies Phagocytosis of fungal spores SEM : Witness nature's defense mechanism unfold as fungal spores are engulfed by cells in a captivating scanning electron microscope (SEM) image.