Cell Biology Collection (page 17)
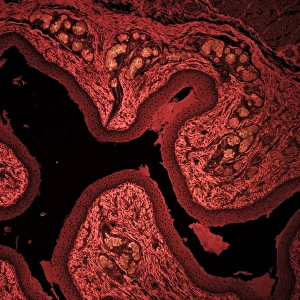
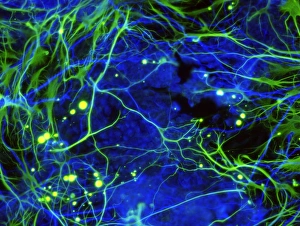
"Exploring the Intricacies of Cell Biology: A Fascinating Journey into Cellular Life" Nerve and glial cells, captured through a mesmerizing light micrograph
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
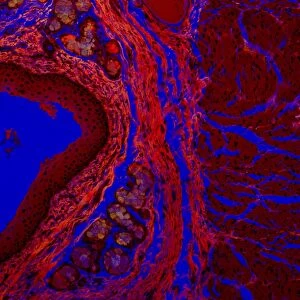
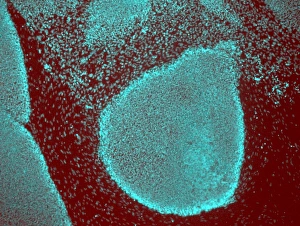
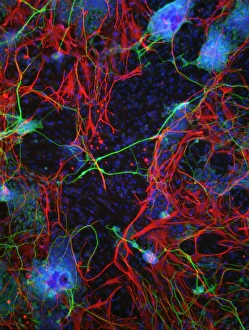
"Exploring the Intricacies of Cell Biology: A Fascinating Journey into Cellular Life" Nerve and glial cells, captured through a mesmerizing light micrograph, reveal the intricate network that supports our nervous system. T lymphocytes battling cancer cells - witness this epic battle in stunning detail with SEM C001 / 1679 imagery. Anaesthetic inhibiting an ion channel - delve into the world of cellular communication as we uncover how anaesthetics affect these vital channels (C015 / 6718). Glial cells take center stage in a captivating confocal light micrograph, showcasing their crucial role in supporting neurons. Witness the beauty of glial stem cell culture under a microscope; it's like exploring an enchanting galaxy within our own bodies (light micrograph). Dendritic cells come to life through exquisite artwork, highlighting their pivotal role in immune response and defense mechanisms. Pine pollen grains unveil their intricate structure under a light microscope – nature's tiny marvels never cease to amaze us. Dive deep into the inner workings of pine stems with a captivating light micrograph – discover the building blocks that support these majestic trees. Explore the hidden wonders of lime tree stems through a mesmerizing light micrograph – witness nature's architectural masterpiece up close. Uncover various cell types brought to life through breathtaking artwork – each one playing its unique part in maintaining life's delicate balance. Immerse yourself in neural stem cell culture and witness firsthand how these remarkable cells hold immense potential for regenerative medicine. The artistic portrayal of cell membranes (C013 / 7467) invites you to ponder upon their crucial role as gatekeepers controlling molecular traffic within living organisms. Embark on this awe-inspiring journey into cell biology and unlock the secrets that shape all living beings from within.