Voltaic Collection
"Unleashing the Power of Voltaic
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
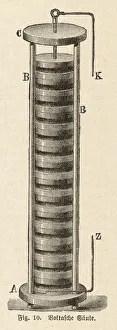
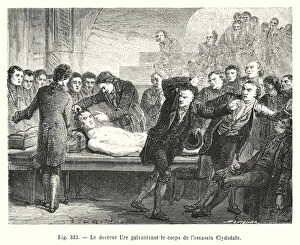
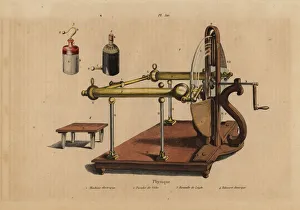
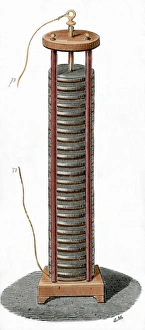
"Unleashing the Power of Voltaic: Exploring the Electrifying World of Alessandro Volta" Step into the electrifying world of Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio Volta (1745-1827), a brilliant Italian physicist whose pioneering work in electricity revolutionized science. Known for his invention of the voltaic pile, an early form of battery, Volta's contributions to electrical research continue to shape our modern understanding. One fascinating application of his voltaic pile was seen in the fruit-powered clock, a marvel that showcased how energy could be harnessed from organic sources. This ingenious creation demonstrated the potential for sustainable power generation long before it became mainstream. Through a colored engraving depicting Volta's iconic voltaic pile, we witness the intricate design and craftsmanship behind this groundbreaking device. Its layered arrangement of metal discs separated by cardboard soaked in saltwater formed an electric circuit capable of producing continuous current – a true testament to Volta's ingenuity. The impact and significance of Volta's work extended beyond mere scientific curiosity. Engravings capturing moments such as Dr. Ure galvanizing Clydsdale's assassin or Halle et de Humboldt replicating Galvani and Volta's experiments highlight how these discoveries influenced medical practices and inspired further exploration into galvanism. Intriguingly, illustrations from Les Merveilles de la Science reveal another innovation stemming from Volta's principles – The Grove cell. Published in 1870, this advancement built upon his original concept by utilizing different chemical reactions to generate electricity more efficiently. Further engravings depict captivating scenes like doctors at Mayence Association conducting experiments on November 21st, 1803 or Larrey inducing muscle contractions through galvanism on recently amputated limbs. These images showcase how far-reaching and impactful Voltian ideas were within various fields.