Vitamin B Collection
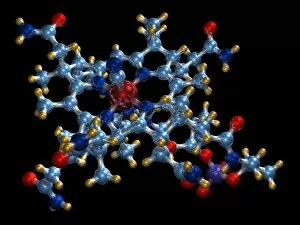
"Unlock the Power of Vitamin B: From Molecular Models to Nutrient-Rich Foods" Vitamin B, a group of essential nutrients vital for our overall well-being
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
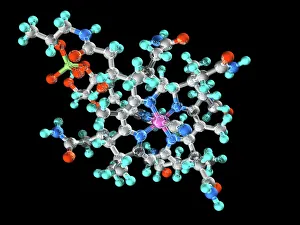
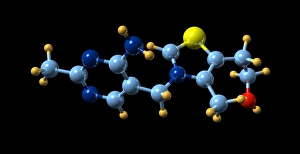
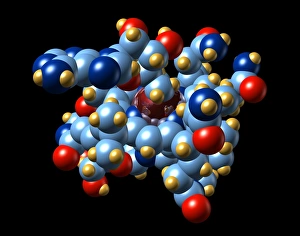
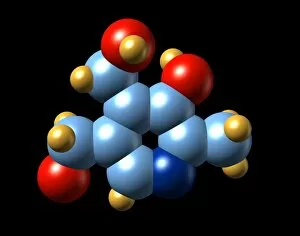
"Unlock the Power of Vitamin B: From Molecular Models to Nutrient-Rich Foods" Vitamin B, a group of essential nutrients vital for our overall well-being, plays a crucial role in maintaining our health. Among its various forms, Vitamin B12 stands out as an important player in energy production and nerve function. Its molecular model reveals the intricate structure that supports these functions. But it's not just about Vitamin B12; there is a wide range of foods rich in different types of vitamin B. Broccoli, broad beans, green beans, mushrooms, lettuce, and yeast extract are some examples that offer this valuable nutrient. A side view showcases their vibrant colors and textures—a feast for both the eyes and body. Papaya also makes an appearance on this journey through vitamin B benefits. Carica papaya contains essential vitamins including vitamin B1 crystals seen under light micrograph—tiny wonders that contribute to metabolism regulation. Speaking of crystals under microscopic lenses, we can't miss exploring the beauty within vitamin B7 crystals. These delicate structures highlight another facet of this remarkable nutrient family. Zooming back into focus on Vitamin B1 crystals once again emphasizes its significance—this time with multiple images capturing its captivating form from different angles. These visuals remind us how nature creates such intricate designs even at a microscopic level. Completing our exploration is Vitamin B5's molecular model—an indispensable component involved in energy production and hormone synthesis processes within our bodies. Ultimately, understanding the molecular models alongside real-world food sources provides insight into why incorporating diverse sources of vitamin Bs is crucial for optimal health. So let's embrace these natural wonders and unlock the power they hold—the power of Vitamin Bs.