Virology Collection (page 2)
Virology, the fascinating study of viruses and their impact on living organisms
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
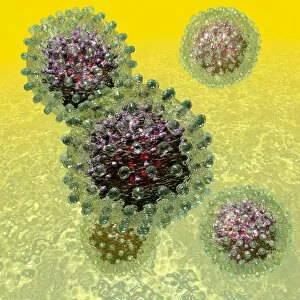
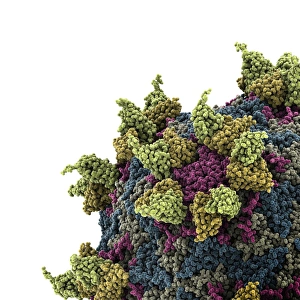
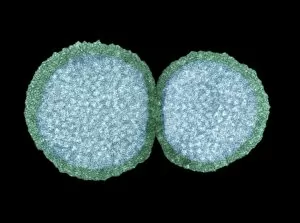
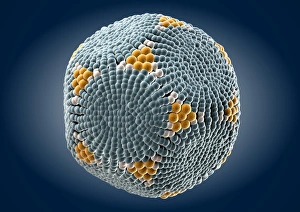
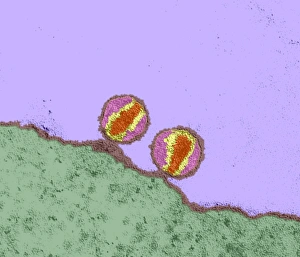
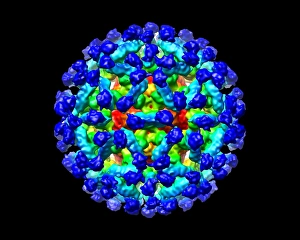
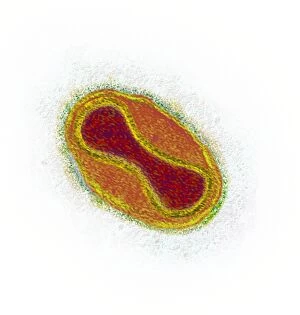
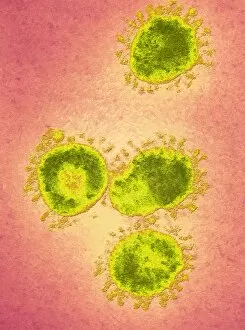
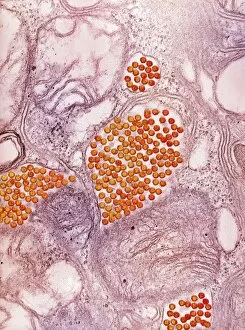
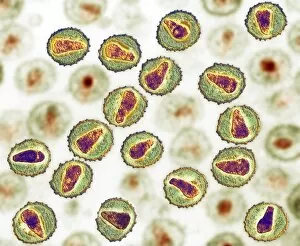
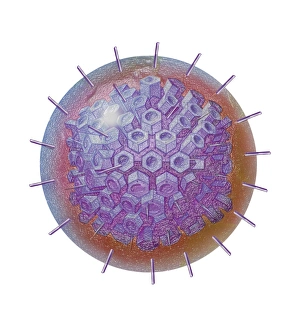
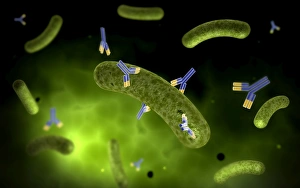
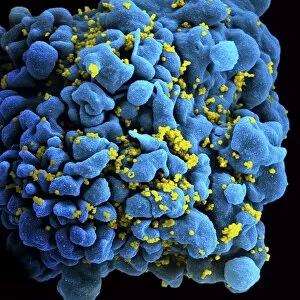
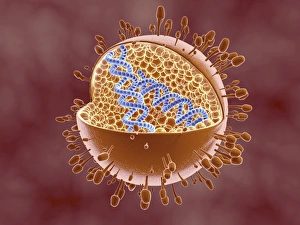
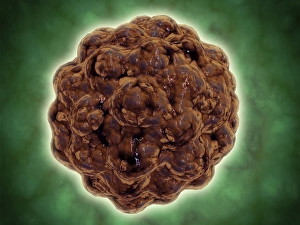
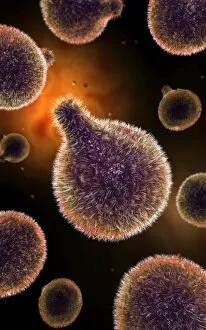
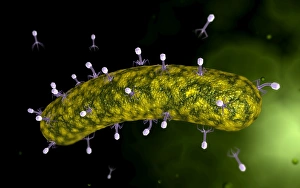
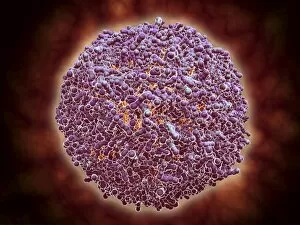
Virology, the fascinating study of viruses and their impact on living organisms, delves into a vast array of viral entities that have shaped our understanding of infectious diseases. From the Avian flu virus to HIV particles, Norovirus particles observed through TEM, and even the intricate workings of HIV reverse transcription enzyme and Hepatitis C virus enzyme molecular models - virologists explore these tiny but powerful agents with great curiosity. The Avian flu virus has long been a concern due to its potential for devastating outbreaks in both avian species and humans. Its ability to jump from birds to humans highlights the ever-present threat posed by zoonotic infections. Similarly, HIV particles continue to challenge researchers as they strive for effective treatments against this relentless retrovirus. Norovirus particles captured under transmission electron microscopy (TEM) reveal their unique structure responsible for causing gastroenteritis outbreaks worldwide. Understanding these minute details aids in developing strategies to combat their spread. Hepatitis B viruses are another focus within virology research due to their significant impact on liver health globally. Molecular models help visualize the complex mechanisms employed by these viruses during infection. Microscopic views of human respiratory syncytial virus remind us of how easily respiratory infections can spread among individuals through coughing or sneezing. Artwork depicting such scenarios serves as a reminder of the importance of hygiene practices in preventing disease transmission. Flu virus particle artwork showcases its distinct appearance while emphasizing its continuous evolution and ability to cause seasonal epidemics worldwide. This visual representation helps scientists comprehend its structure better when designing vaccines each year. Coronavirus particles imaged using TEM highlight recent concerns surrounding emerging viral threats like SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19. The ongoing pandemic underscores the urgency for further virological studies aimed at combating future outbreaks effectively. Lastly, adenoviruses capture attention with artistic renditions showcasing their structural intricacies while reminding us that not all viruses are harmful.