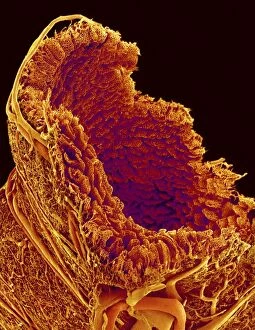
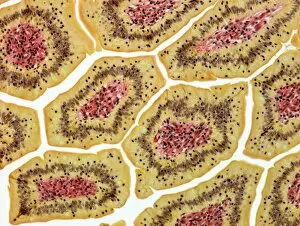
Villi Collection
Villi: The Tiny Heroes of the Human Digestive System In the intricate world of the human digestive system, there exists a remarkable structure known as villi
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
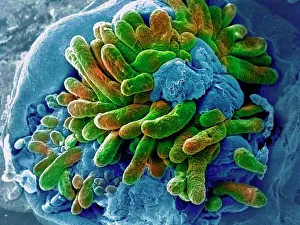
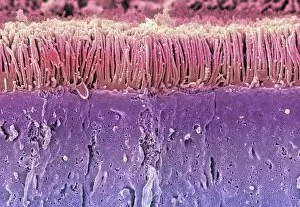
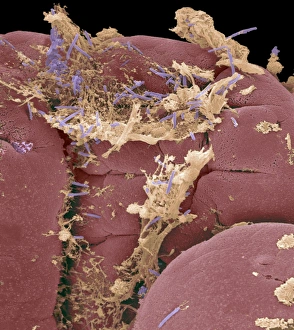
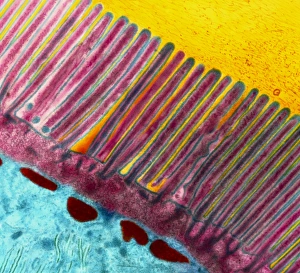
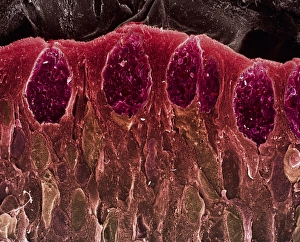
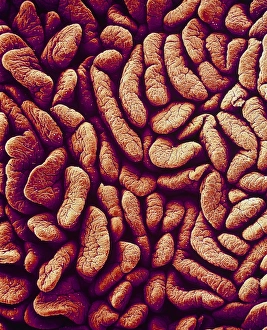
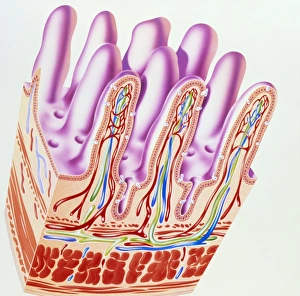
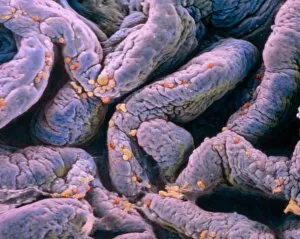
Villi: The Tiny Heroes of the Human Digestive System In the intricate world of the human digestive system, there exists a remarkable structure known as villi. These small finger-like projections line the walls of our small intestine, playing a crucial role in nutrient absorption and digestion. Through scanning electron microscopy (SEM), we can witness the stunning beauty of these microscopic heroes up close. Picture No. 10877012 captures their delicate intricacy, resembling an artistic masterpiece created by nature itself. But what exactly do these villi do? Imagine Maja Bublao from Croatia with her beloved Clumber Spaniel named Villi, who triumphantly claimed the title of Best of Breed winner at Crufts 2023 held at NEC Birmingham on Thursday 09. 03. 23. Just like this adorable canine champion, intestinal it can winners too. Their main task is to increase surface area within our small intestine, allowing for efficient absorption of nutrients into our bloodstream. This process ensures that vital substances such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are properly digested and utilized by our bodies. Not only do they enhance nutrient absorption but also protect against harmful invaders lurking within our gut ecosystem. Think about it - just like how colorectal cancer cells can be observed under SEM revealing their sinister appearance; intestinal villi act as defenders against such threats. The artwork depicting intestinal lining showcases their unique architecture - tall columns covered in microvilli that resemble tiny bristles ready to catch any valuable nutrients passing through. Underneath a light microscope's lens lies another breathtaking view - a mesmerizing image capturing the vibrant colors and intricate patterns found in healthy small intestines. However, when diseases like colorectal cancer strike, these brave warriors may become compromised or damaged due to abnormal cell growth seen under SEM once again. Let us appreciate these unsung heroes residing within us – those magnificent villi working tirelessly day after day to ensure proper digestion and absorption. Their vital role in maintaining our overall health cannot be overstated.