Vesicles Collection
Vesicles: Tiny Transporters in the Intricate World of Cells In the fascinating realm of cellular biology, vesicles play a crucial role as miniature transporters
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
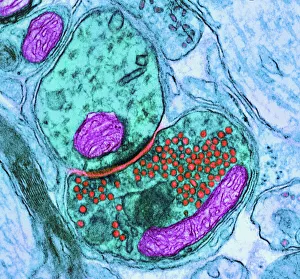
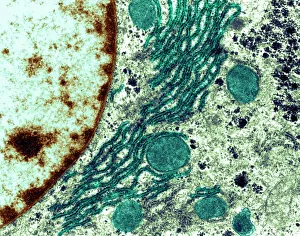
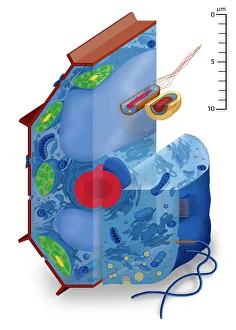
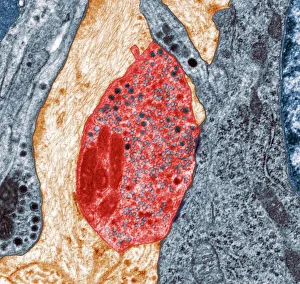
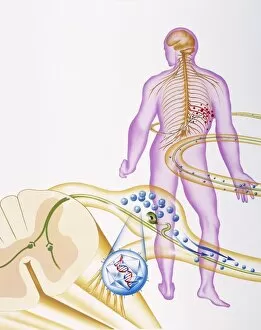
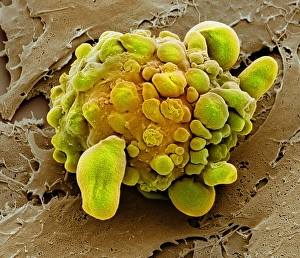
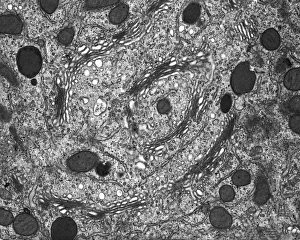
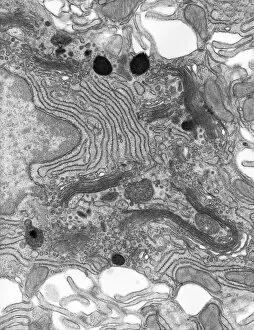
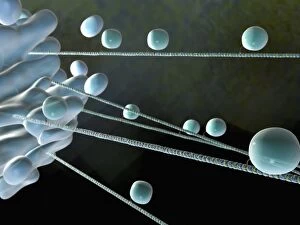
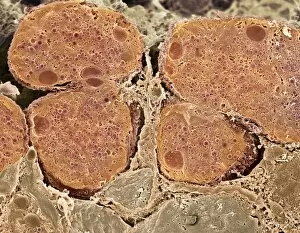
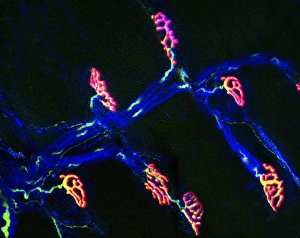
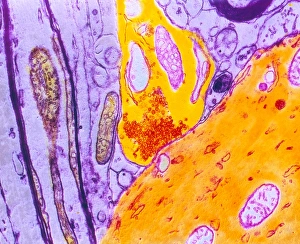
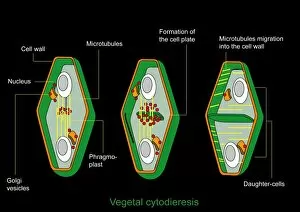
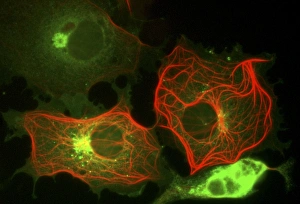
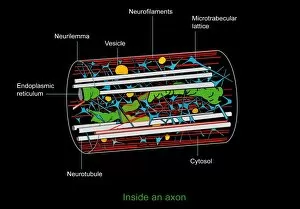
Vesicles: Tiny Transporters in the Intricate World of Cells In the fascinating realm of cellular biology, vesicles play a crucial role as miniature transporters, shuttling vital substances within cells and ensuring their proper functioning. These tiny sacs are involved in various processes, from synapse nerve junctions to protein synthesis. Under the powerful lens of a transmission electron microscope (TEM), we can observe vesicles at work. At synapse nerve junctions, these dynamic structures facilitate communication between neurons by transmitting chemical signals. The TEM reveals their intricate network, highlighting their significance in maintaining healthy neural connections. Another intriguing sight captured by TEM is the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER). This labyrinthine structure studded with ribosomes produces proteins destined for export or insertion into cell membranes. Vesicles bud off from this ER network, carrying newly synthesized proteins to different parts of the cell. Cell types come alive through captivating artwork depicting fibroblast cells and protein interactions with microtubules. These illustrations showcase how vesicles collaborate with other cellular components to ensure proper functioning and organization within cells. The Golgi apparatus takes center stage under scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Its distinctive appearance resembles a stack of flattened pancakes and serves as an important processing center for proteins before they are packaged into vesicles for transportation throughout the cell. Nasal lining viewed through SEM provides insight into its complex structure and highlights how vesicles contribute to maintaining respiratory health. Additionally, shingles nerve damage reminds us that disruptions in vesicle transport can lead to severe consequences such as pain and discomfort. A detailed model of an animal cell offers a comprehensive view of various organelles including nuclei, golgi bodies, lysosomes, centrioles, mitochondria - all interconnected by a vast network of endoplasmic reticulum. Vesicles stand out among these essential components as key players responsible for transporting molecules across different compartments within the cell.