Vacuole Collection
The vacuole, a vital organelle found in various organisms, plays diverse roles in their survival and functioning
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
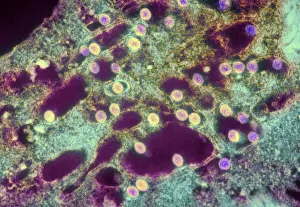
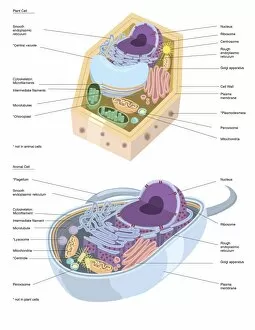
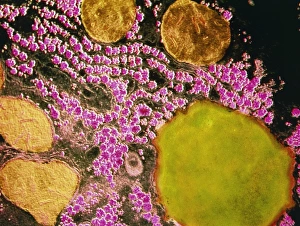
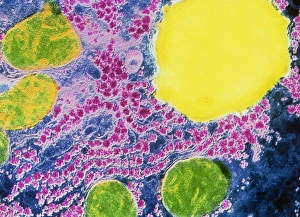
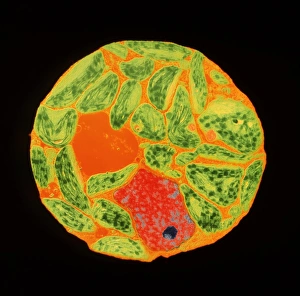
The vacuole, a vital organelle found in various organisms, plays diverse roles in their survival and functioning. From protecting against harmful pathogens to maintaining cell structure, the vacuole is truly remarkable. In Rift Valley fever virus-infected cells observed through Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), the vacuole acts as a defensive fortress. It encapsulates the virus particles, preventing their spread and minimizing damage to surrounding cellular components. Similarly, Coxiella burnetii, the bacterium responsible for Q Fever, finds itself confined within vacuoles. This containment prevents its replication and ensures host defense mechanisms can effectively neutralize it. Yeast cells under TEM reveal an intriguing aspect of the vacuole's functionality. These single-celled organisms utilize this organelle as a storage compartment for nutrients such as amino acids and sugars. The vacuole acts like a pantry that yeast cells tap into during times of scarcity or stress. Illustrations showcasing plant cell structures highlight how central the vacuole is to their existence. Alongside prominent features like the nucleus, nucleolus, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and other organelles; plant cells possess large central vacuoles that maintain turgor pressure crucial for structural support. Microscopic views provide glimpses into intricate details of different organisms' cellular makeup. In plants specifically, stomata are conceptualized - tiny openings on leaves where gas exchange occurs with environmental factors regulated by specialized guard cells flanking them. Comparatively speaking between plant and animal cell anatomy reveals distinct differences in their respective vacuolar systems. While plant cells boast one or more significant central vacuoles occupying most of their interior space; animal cells contain smaller vesicles scattered throughout without any centralized structure. Lastly but not leastly paramecium - these unicellular eukaryotes exhibit contractile vacuoles responsible for osmoregulation by expelling excess water.