Trna Collection
TRNA, also known as transfer RNA, is a crucial molecule involved in protein synthesis
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
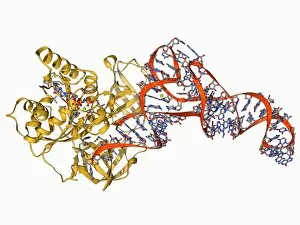
TRNA, also known as transfer RNA, is a crucial molecule involved in protein synthesis. It plays a vital role in the translation of genetic information from DNA to proteins. The tRNA molecule acts as an adapter between the mRNA (messenger RNA) and amino acids during protein synthesis. It carries specific amino acids to the ribosome, where they are joined together to form a polypeptide chain. Working in conjunction with the Transfer RNA-synthetase complex molecule, tRNA ensures that each amino acid is correctly matched with its corresponding codon on the mRNA strand. This process requires precise recognition and binding by enzymes such as Tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase molecule and Tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase molecule. In addition to its role in protein synthesis, it has been found to interact with various other molecules within the cell. For example, Ribonuclease can bind to transfer RNA, potentially affecting its stability or function. Furthermore they can associate with Elongation factor Tu during elongation of the growing polypeptide chain on the ribosome. This interaction helps facilitate efficient protein synthesis. Different types of tRNAs exist for each amino acid due to their specificity towards particular codons on mRNA strands. Valyl-tRNA synthetase molecule and Isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase molecule are enzymes responsible for attaching valine and isoleucine respectively onto their respective tRNAs (Valyl-tRNA synthetase F006 / 9342 & Isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase F006 / 9329).