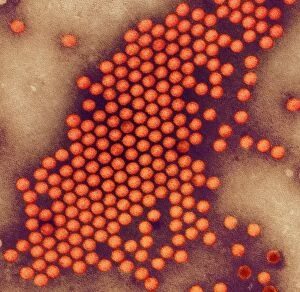
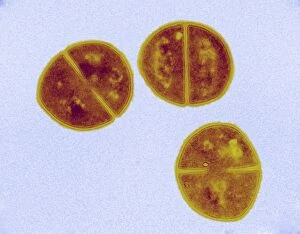
Transmission Electron Microscope Collection
The transmission electron microscope (TEM) has revolutionized our understanding of the intricate world within our bodies
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
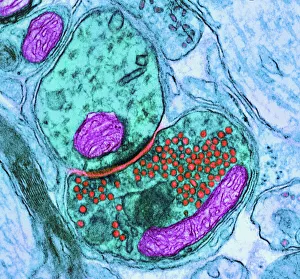
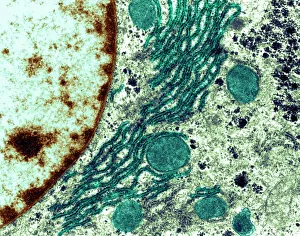
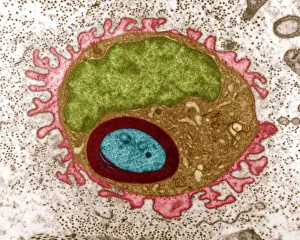
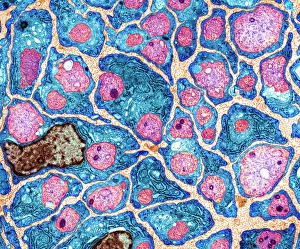
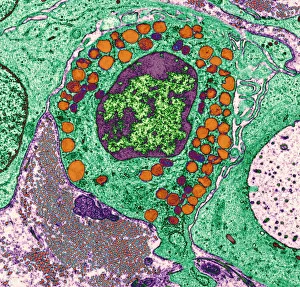
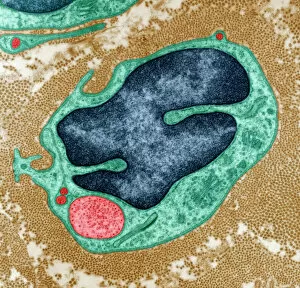
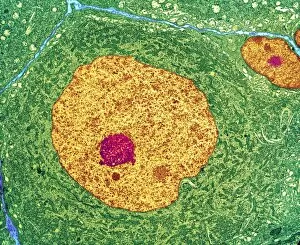
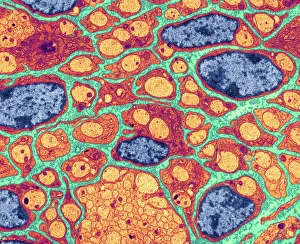
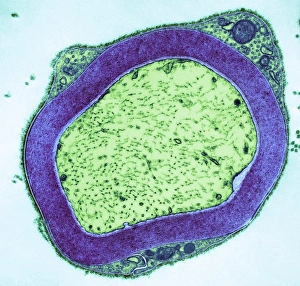
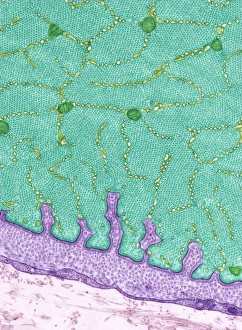
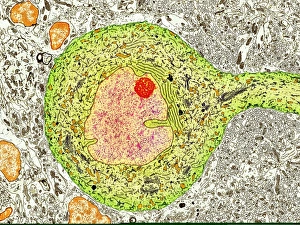
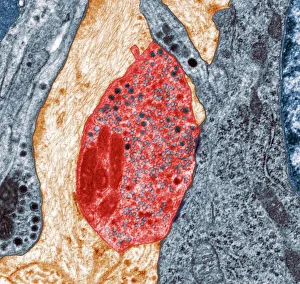
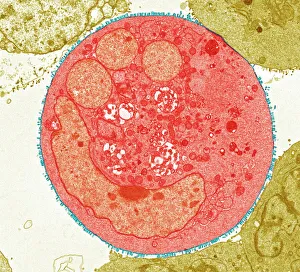
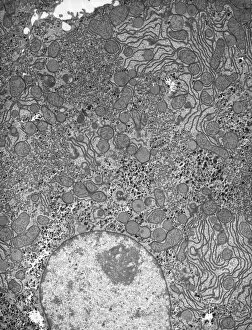
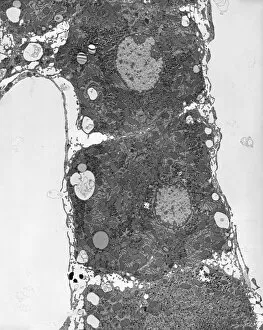
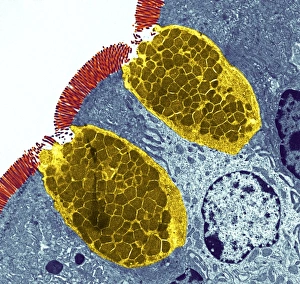
The transmission electron microscope (TEM) has revolutionized our understanding of the intricate world within our bodies. With its high-resolution imaging capabilities, it allows us to delve deep into the microscopic realm and explore various cellular structures and processes. In the synapse nerve junction, TEM reveals a complex network of connections between neurons, highlighting their crucial role in transmitting signals throughout the nervous system. The rough endoplasmic reticulum, as seen through TEM, showcases its ribosome-studded surface responsible for protein synthesis. Witnessing a regenerating nerve cell under TEM provides insight into the remarkable ability of these cells to repair and restore function after injury. Meanwhile, observing a basophil white blood cell with this powerful microscope sheds light on its involvement in immune responses against allergens and parasites. TEM also unravels the fascinating process of myelination of nerve fibers - an essential mechanism for efficient signal conduction. Through detailed images captured by TEM, we can observe how myelin sheaths wrap around nerve fibers like protective insulation. Exploring further into nerve cells using TEM exposes their intricate structure comprising dendrites, axons, and synaptic terminals that enable communication within the nervous system. Additionally, mitochondria – often referred to as "the powerhouse of the cell" – are revealed in astonishing detail through TEM's lens. With precise imaging capabilities offered by TEM C014 / 1468, we can examine eye muscles at an unprecedented level. This aids in understanding their unique properties related to movement and coordination. Finally, studying Purkinje nerve cells with TEM C014 / 0583 allows us to appreciate their distinctive morphology within cerebellar tissue – characterized by elaborate branching patterns that contribute to motor coordination. In summary, transmission electron microscopy opens up a whole new dimension in biology research by providing unparalleled insights into cellular structures such as synapses, endoplasmic reticulum dynamics or regeneration processes while unraveling mysteries surrounding immune responses or myelination.