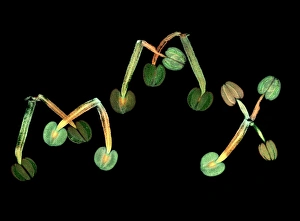Thale Cress Collection
"Exploring the Intricate World of Thale Cress: Arabidopsis thaliana" Delve into the fascinating realm of Thale cress
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
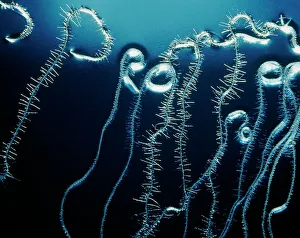
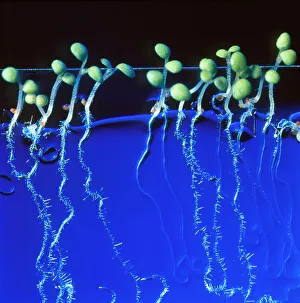
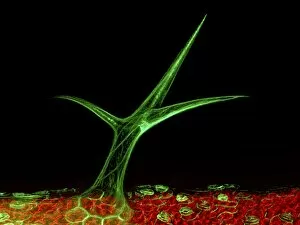
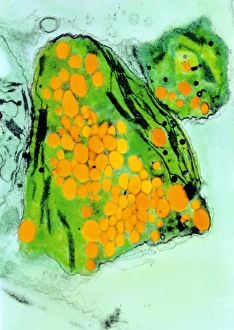
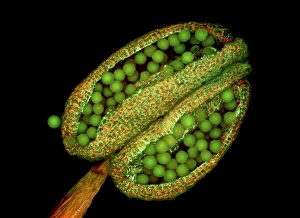
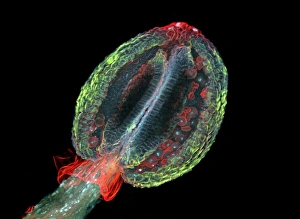
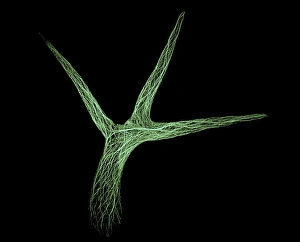
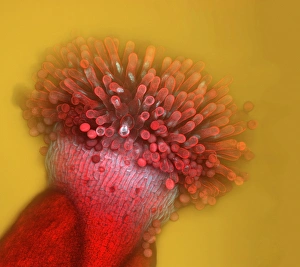
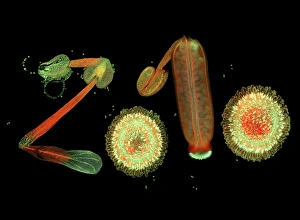
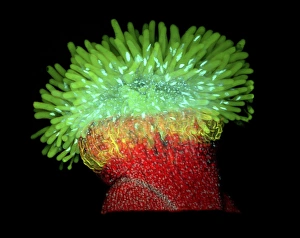
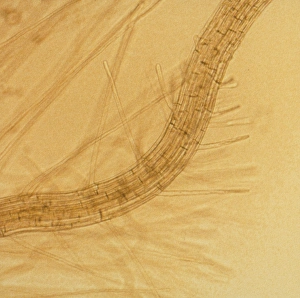
"Exploring the Intricate World of Thale Cress: Arabidopsis thaliana" Delve into the fascinating realm of Thale cress, also known as Arabidopsis thaliana or mouse-ear cress. This small but mighty plant has captivated botanists and researchers alike with its remarkable features. At first glance, you may notice its delicate roots firmly anchoring it to the ground, providing stability and nourishment for this cultured cress plant. Moving upwards, a vibrant micrograph reveals the intricate beauty flowers in all their glory. Arabis thaliana, another name for this versatile species, is depicted in an antique engraving illustration alongside Cardamine (bittercress), showcasing the rich history and significance of these plants. Furthermore, molecular model F006/9545 highlights how Thale cress acts as a vital plant hormone regulator. Zooming in closer under a scanning electron microscope (SEM), we witness the mesmerizing details leaf stomata (C016/9460 & C016/9459). These microscopic structures play a crucial role in gas exchange and transpiration within the plant's leaves. An enchanting illustration (C018/0729) encapsulates the essence – its slender stems adorned with lush foliage that adds charm to any botanical landscape. Moreover, scientists have delved into researching plant odors using this intriguing specimen. Examining further aspects of this extraordinary plant kingdom brings us to explore Thale cress anthers and pollen - essential components for reproduction. Additionally, fluorescent micrographs unveil captivating patterns on Trichomes – tiny hair-like structures found on various parts of plants including our star subject here. Thoroughly studying every aspect from root to trichome allows us to appreciate both the aesthetic allure and scientific significance behind "Thale Cress: Arabidopsis thaliana.