Round Worm Collection (page 2)
The round worm, also known as the nematode worm, is a fascinating creature that comes in various forms. One of the most well-known species is C
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
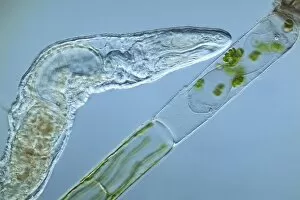
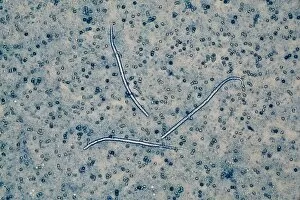
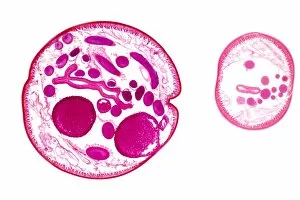
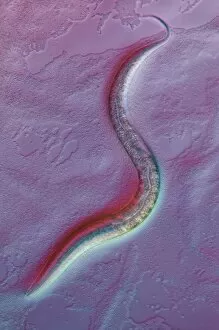
The round worm, also known as the nematode worm, is a fascinating creature that comes in various forms. One of the most well-known species is C. Elegans, which has been extensively studied in scientific research. Through light micrographs and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), we can observe the intricate details of these worms. In one image captured by SEM, we see a nematode worm with its elongated body and distinct features. These parasitic nematodes are notorious for causing diseases in humans and animals alike. Their ability to adapt and survive in different environments is truly remarkable. Another light micrograph showcases roundworm germ cells under magnification. The delicate structures within these cells highlight their importance in reproduction and genetic diversity. Similarly, another image reveals more roundworm germ cells, emphasizing their significance in the life cycle of these organisms. Moving on to C. Elegans specifically, an LM image provides us with a closer look at this model organism's anatomy. Its transparent body allows researchers to easily study its internal organs and developmental processes. Artwork depicting Ascaris sp. , a type of nematode worm found in the human intestine, gives us an artistic representation of these creatures' presence within our bodies. This serves as a reminder that not all interactions between humans and worms are beneficial or harmless. Brugia malayi is another example of a parasitic nematode worm that causes human filariasis - a debilitating disease affecting millions worldwide. A light micrograph captures its structure, highlighting the need for further research into prevention methods and treatments for such infections. Lastly, an SEM image shows false coloration applied to showcase a nematode worm found on peat samples – demonstrating how diverse these organisms can be even when living within seemingly inhospitable environments.