Ptolemy Collection (page 4)
"Ptolemy: Unraveling the Mysteries of the Universe through Time" Step into the world of Ptolemy
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
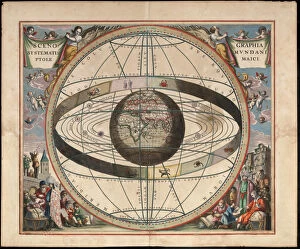
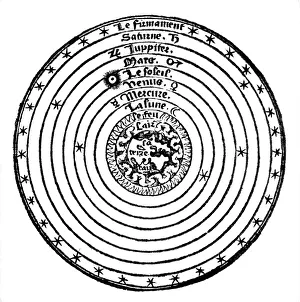
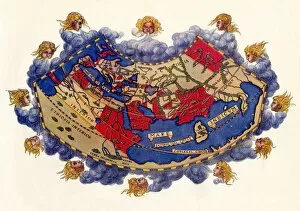
"Ptolemy: Unraveling the Mysteries of the Universe through Time" Step into the world of Ptolemy, a renowned ancient astronomer and geographer whose contributions shaped our understanding of the cosmos. From Johannes Kepler's model of the universe to Oronce Fine's intricate world map, Ptolemy's influence spans centuries. In Raphael's masterpiece "The School of Athens, " we catch a glimpse amidst esteemed philosophers, his ideas resonating with scholars even in 1510. His groundbreaking work is further showcased in Claudius Ptolemy's Map of the World from AD 150, an impressive testament to his cartographic skills. Marvel at Andreas Cellarius' copperplate engraving where Copernicus and Ptolemy stand side by side, representing two contrasting views on celestial motion. With the sun at its center, this depiction challenges Ptolemaic beliefs but acknowledges their historical significance. Delve deeper into Ptolemy's legacy as you explore Northern hemisphere star charts and discover worlds known to him during his time. Witness how he meticulously constructed his system that explained planetary movements with precision and elegance. But perhaps one cannot speak about Ptolemy without mentioning Cleopatra - their names forever intertwined in history. The grandeur of their reigns immortalized on walls that tell tales of power and love. Lastly, let us not forget the legendary Library of Alexandria - a beacon for knowledge seekers throughout antiquity. It was here that countless manuscripts were preserved, including works by none other than Claudius Ptolemaeus himself. Pioneering both astronomy and geography during an era when exploration was limited, Ptolemy left an indelible mark on scientific thought. As we gaze upon these artifacts from different eras, we are reminded that human curiosity knows no bounds – always seeking answers to unravel mysteries yet unknown.