Polarised Light Microscopy Collection
"Polarised Light Microscopy: Revealing the Intricate Beauty of Nature's Structures" Delving into the microscopic world
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
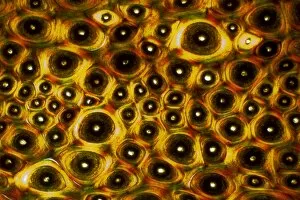
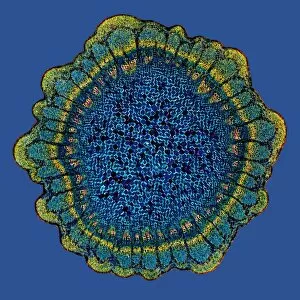
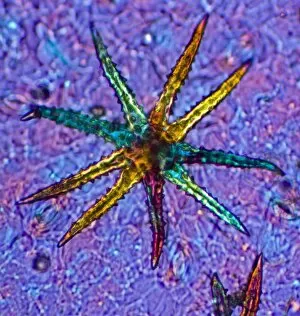
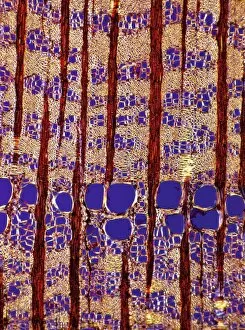
"Polarised Light Microscopy: Revealing the Intricate Beauty of Nature's Structures" Delving into the microscopic world, polarised light microscopy unveils mesmerizing details hidden within various natural specimens. The water fern rhizome, captured in a stunning light micrograph, showcases its intricate network of roots and shoots. Each delicate strand intertwines to support this aquatic plant's growth and survival. Whale bone tissue, illuminated under polarised light, reveals a captivating mosaic-like pattern. This unique micrograph provides insights into the composition and structure of these majestic creatures' skeletal framework. In another striking image of whale bone tissue, polarised light microscopy exposes an array of vibrant colors dancing across the surface. These hues signify different mineral deposits that have accumulated over time, offering clues about the whale's life history. A grape vine stem exhibits its remarkable complexity when examined through polarised light microscopy. The interwoven fibers form an elegant lattice that enables this plant to thrive and bear fruit. Stellate plant hair takes center stage in yet another breathtaking micrograph captured using polarised light. Its star-shaped silhouette glistens with iridescent beauty as it adorns leaves or stems for protection against predators or environmental stressors. Tree growth rings present a fascinating story etched within their concentric circles when observed under polarised light. Each ring signifies a year's worth of growth and holds valuable information about climatic conditions during that period. Pine tree stems showcase their resilience through intricate patterns unveiled by polarised light microscopy. The dense arrangement of cells contributes to their strength and ability to withstand harsh weather conditions. The mollusc radula captivates with its intricately arranged teeth structures when viewed through polarized light microscopy. This feeding organ offers insight into how these marine creatures adapt to diverse diets in their underwater habitats. Virginia creeper stem displays its elegance under the lens of polarized light microscopy—an enchanting tapestry woven by nature.