Plastids Collection
Plastids, the versatile organelles found in plant cells, play a crucial role in various cellular processes
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
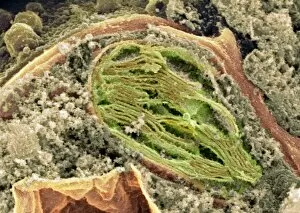
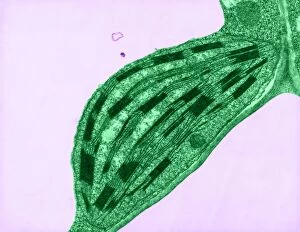
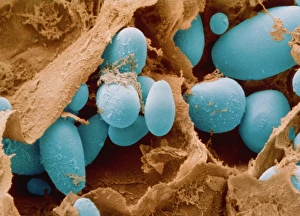
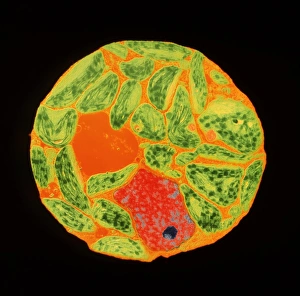
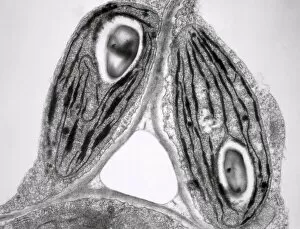
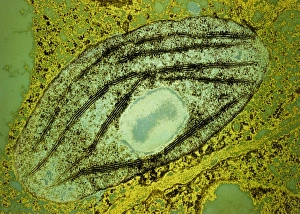
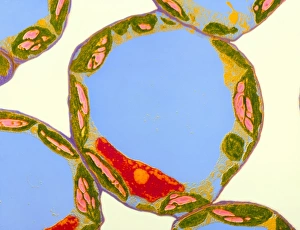
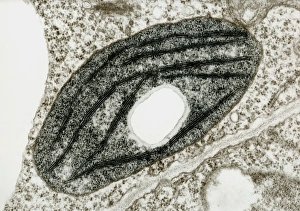
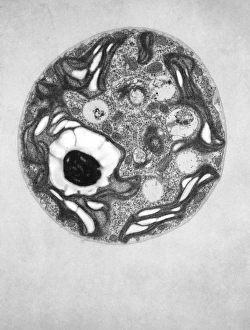
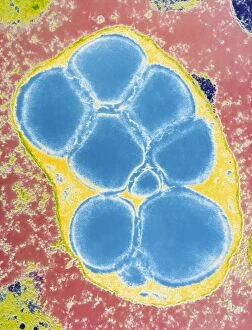
Plastids, the versatile organelles found in plant cells, play a crucial role in various cellular processes. One of the most well-known types of the chloroplast, which can be observed within the cells of a pea plant. Under scanning electron microscopy (SEM), these chloroplasts reveal their intricate structures and mesmerizing beauty. The detailed images captured by TEM C016 / 6297, TEM C016 / 6298, and TEM C017 / 8233 showcase the inner workings of chloroplasts with astonishing clarity. Apart from their visual appeal, it also serve important functions within plants. Starch grains derived from potato cells are an excellent example of how plastids store energy reserves for future use. These starch grains are easily identifiable under microscopic examination and provide insights into plant metabolism. In addition to their functional significance, they have captivated artists who have depicted them through stunning artwork that showcases their unique shapes and patterns. Even under SEM imaging techniques specifically designed to study surface features, such as those seen in Chloroplast SEM images or Plant cell SEM images, these organelles continue to inspire awe. Overall, studying plastids not only enhances our understanding of plant biology but also allows us to appreciate nature's intricate designs at a microscopic level. From chloroplasts' vital role in photosynthesis to starch grain storage mechanisms and even artistic interpretations - this diverse range highlights just how fascinating and essential plastids truly are for life on Earth.