Pathogens Collection
"Unseen Threats: Exploring the World of Pathogens" Nature's Battle: A tobacco hornworm feasting on a tobacco plant
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
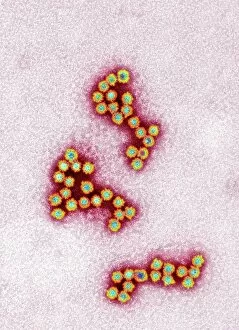
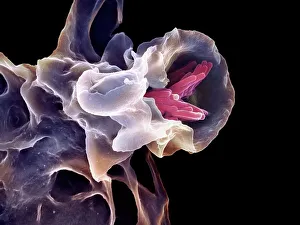
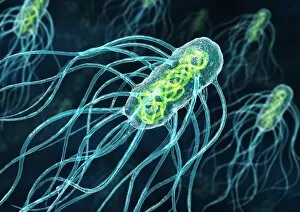
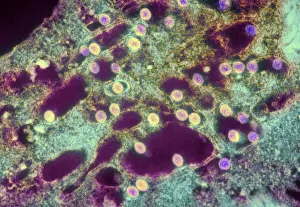
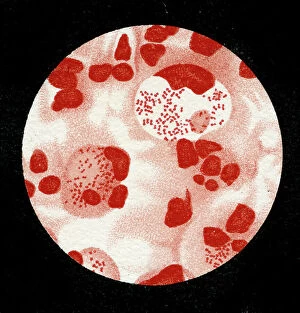
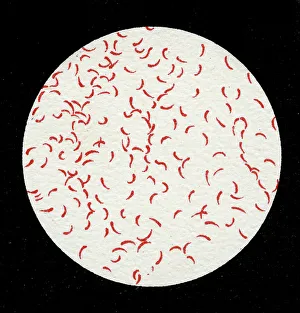
"Unseen Threats: Exploring the World of Pathogens" Nature's Battle: A tobacco hornworm feasting on a tobacco plant, showcasing the intricate relationship between pathogens and their hosts. Fungal Invasion: Coral Spot Fungus (Nectria cinnabarina) fruiting bodies thriving on a Sycamore twig in Powys, Wales – a reminder of how they are infiltrate even the hardiest organisms. Tiny Terrors: Norovirus particles captured under an electron microscope, revealing the minuscule yet potent nature of these infectious agents. The Silent Killer: Tuberculosis bacteria lurking within our midst, highlighting the ongoing battle against this ancient disease that still plagues humanity today. Unwelcome Guests: Salmonella bacteria magnified through scanning electron microscopy, serving as a stark reminder of foodborne illnesses and their potential consequences. Airborne Hazards: Artwork depicting infections spread by sneezing – emphasizing how easily they are travel and infect others within close proximity. Cellular Warriors: Macrophage engulfing TB bacteria showcased under SEM, illustrating our immune system's relentless fight against invading pathogens. Invisible Invaders: Intestinal protozoan parasites seen through transmission electron microscopy; uncovering the hidden world where these microscopic creatures wreak havoc on human health. Waterborne Nightmare: Cryptosporidium protozoa viewed under TEM – shedding light on water-related diseases caused by these resilient parasites that pose risks to both humans and animals alike. Emerging Perils: Rift Valley fever virus particles revealed through TEM imagery; underscoring the constant threat posed by emerging viruses with potentially devastating consequences for global health security. Mosquito Menace: Dengue fever virus particles visualized using TEM; reminding us of mosquito-borne diseases' impact worldwide and efforts to combat them effectively. The Immune Battle Continues.