Pathogen Collection (page 7)
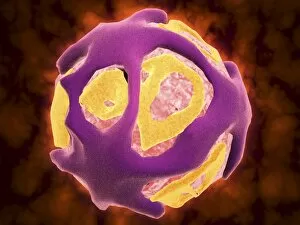
"Unseen Threats: Exploring the World of Pathogens" Budding yeast cell: A microscopic powerhouse, capable of causing infections in humans and animals alike
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
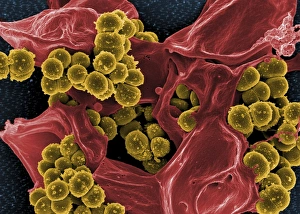
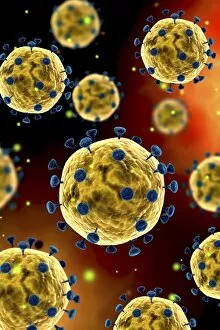
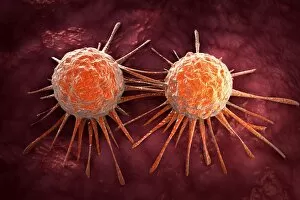
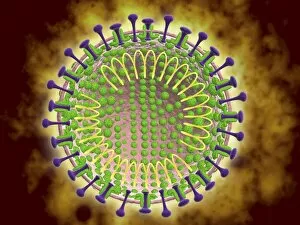
"Unseen Threats: Exploring the World of Pathogens" Budding yeast cell: A microscopic powerhouse, capable of causing infections in humans and animals alike. Avian flu virus: A notorious pathogen that poses a significant threat to both birds and humans, with potential for devastating global outbreaks. Neutrophil engulfing MRSA, SEM C018 / 8596: Witness the incredible defense mechanism of our immune system as it battles against antibiotic-resistant bacteria. E. Coli bacteria, SEM: Unveiling the minuscule culprits behind foodborne illnesses and urinary tract infections. Salmonella bacteria, SEM: Discover the intricate structure of this common bacterial pathogen responsible for causing severe gastrointestinal distress. Candida fungus, SEM: Peering into the world of fungal infections as Candida takes center stage in various ailments from thrush to systemic candidiasis. Coral Spot Fungus (Nectria cinnabarina) fruiting bodies on Sycamore twig, Powys, Wales: Marvel at nature's ability to harbor pathogens even within picturesque settings like these vibrant red fruiting bodies growing on trees. HIV particle: Delve into the complex realm of retroviruses with a focus on HIV/AIDS – an ongoing global health crisis demanding attention and research breakthroughs. Anthrax cultures, historical diagram: Tracing back through history to understand one of humanity's oldest known pathogens – anthrax – its deadly impact and potential bioweapon applications throughout time. Norovirus particles, TEM: Get up close with these tiny viral particles responsible for stomach flu outbreaks worldwide; their resilience challenges public health measures constantly. Tuberculosis bacteria - Explore the persistent Mycobacterium tuberculosis that causes tuberculosis disease affecting millions globally despite medical advancements Avian flu virus - Investigate avian influenza viruses' ability to jump species barriers, posing a constant threat to both birds and humans.