Octamer Collection
Octamer refers to a crucial component in the intricate world of molecular biology
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
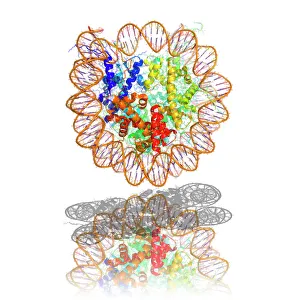
Octamer refers to a crucial component in the intricate world of molecular biology. Specifically, it is associated with nucleosomes, which are fundamental units of DNA packaging within our cells. These nucleosome molecules, such as F006/9323, F006/9314, and F006/9235, play a vital role in organizing and condensing DNA strands. At its core, an octamer consists of eight proteins known as histones that form a complex structure. This octameric unit binds tightly to the DNA molecule, creating what is called a nucleosome core particle bound to DNA. This binding helps regulate gene expression by controlling access to genetic information encoded in the DNA sequence. Interestingly enough, this concept extends beyond just regular cellular processes. Even viruses like Ebola possess matrix protein molecules that interact with host cell components like nucleosomes for their survival and replication purposes. Furthermore, another variant of the nucleosome core particle bound to DNA exists: C014/0872. It showcases how diverse these structures can be while maintaining their essential function. Intriguingly contrasting this topic is RNA interference viral suppressor - an element involved in inhibiting our body's natural defense mechanism against viral infections.