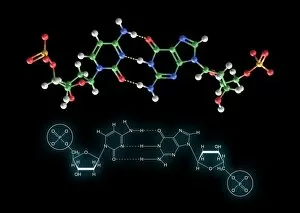
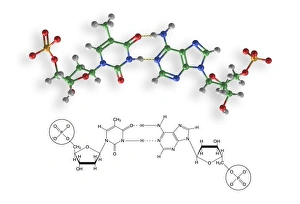
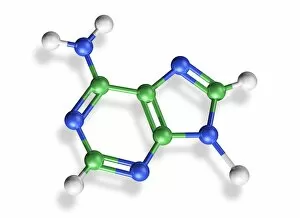
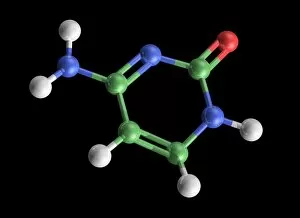
Nucleobase Collection
"Nucleobase: The Building Blocks of Life's Genetic Blueprint" In this captivating collage
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
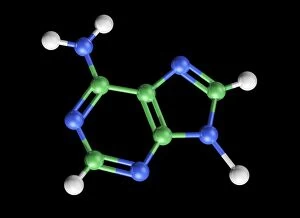
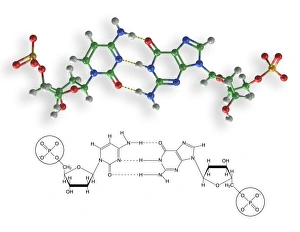
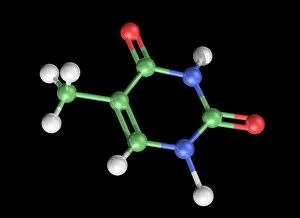
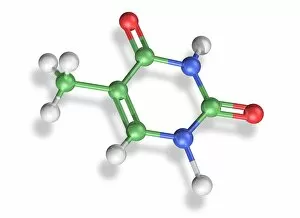
"Nucleobase: The Building Blocks of Life's Genetic Blueprint" In this captivating collage, we embark on a visual journey into the intricate world of nucleobases - the fundamental components that shape our DNA. Conceptual images of DNA strands gracefully intertwine, symbolizing the elegance and complexity inherent in these tiny molecules. At first glance, we are drawn to a mesmerizing microscopic view showcasing the binding process between nucleobases within DNA. Like puzzle pieces fitting perfectly together, these minuscule entities form an exquisite tapestry that encodes life's instructions. Moving forward, conceptual images reappear, reminding us of the overarching significance of nucleobases in shaping our genetic heritage. Their arrangement within DNA determines our unique traits and characteristics; they hold the key to unlocking mysteries buried deep within ourselves. Another glimpse through the microscope reveals an even closer look at how nucleobases interact with one another. We witness their delicate dance as they establish bonds crucial for maintaining stability and transmitting vital information during replication and protein synthesis. Returning to conceptual imagery once more, we are reminded that every living organism shares this common thread – a remarkable testament to nature's ingenuity. Nucleobases serve as unifying elements across species boundaries, connecting all forms of life through their universal presence in DNA. As we conclude this visual exploration, it becomes clear that they are not merely chemical compounds but rather guardians of life's blueprint. They embody both fragility and resilience while holding immense power over our existence. Through their unwavering presence in every cell nucleus lies humanity’s shared story - written by these extraordinary building blocks known as nucleobases.