Nuclear Physics Collection
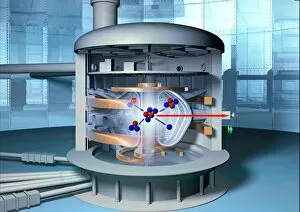
"Nuclear Physics: Unveiling the Mysteries of the Atomic World" Tokamak-15 Nuclear Fusion Reactor C013 / 1348: Pushing the boundaries of energy generation
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
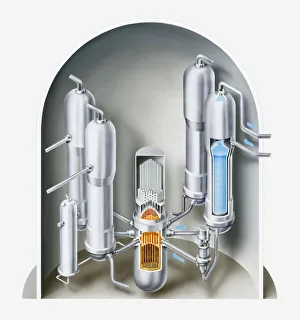
"Nuclear Physics: Unveiling the Mysteries of the Atomic World" Tokamak-15 Nuclear Fusion Reactor C013 / 1348: Pushing the boundaries of energy generation, scientists strive to unlock the potential of fusion power through innovative technologies like Tokamak-15. Tsar Bomba Nuclear Weapon Display: A chilling reminder of humanity's capacity for destruction, this display showcases the immense power and devastating consequences of nuclear weapons. JJ Thomson - Pioneering British Nuclear Physicist (1898): Celebrating the groundbreaking work of JJ Thomson, whose experiments with cathode rays led to revolutionary discoveries about atomic structure and laid the foundation for modern nuclear physics. James Chadwick - Unraveling Neutrons' Mystery (C017 / 7111): Paying tribute to James Chadwick's remarkable discovery of neutrons, a crucial step in understanding atomic nuclei and unlocking new realms within nuclear physics. Particle Collision: Witnessing particles collide at incredible speeds within particle accelerators allows scientists to study fundamental forces and unravel nature's deepest secrets on a subatomic level. Ernest Rutherford - Architect of Modern Atomic Theory (c1908): Commemorating Ernest Rutherford's pioneering contributions that revolutionized our understanding of atoms, leading him to win a Nobel Prize in recognition of his groundbreaking research in nuclear physics. The Powerhouse - Particle Accelerator: Showcasing cutting-edge technology used in particle accelerators, which enable physicists worldwide to explore uncharted territories within nuclear physics by propelling particles at mind-boggling speeds. Nuclear Fusion Conceptual Artwork: Imagining a future where clean and abundant energy is harnessed through controlled nuclear fusion reactions – an aspiration that continues to drive scientific advancements in this field today. Portrait of Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937) 1932 (Oil on Canvas).