Nosocomial Collection
"Unseen Threats: Exploring the World Infections" In the microscopic realm
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
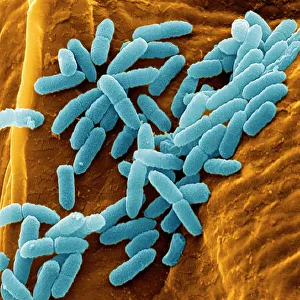
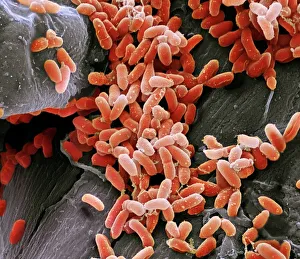
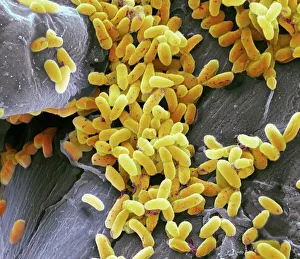
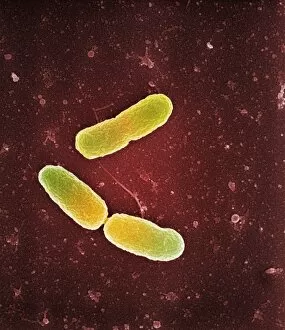
"Unseen Threats: Exploring the World Infections" In the microscopic realm, Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria reveal their intricate structures under the scanning electron microscope (SEM). These formidable organisms, known for their resilience and adaptability, pose a significant risk in nosocomial infections. Moving closer into focus, we encounter Staphylococcus aureus MRSA bacteria C014/2577. This strain is notorious for its resistance to multiple antibiotics, making it a challenging adversary within healthcare settings. Its presence serves as a reminder of the constant battle against these resilient pathogens. Zooming further into another SEM image reveals Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria C017/7140. Their unique features highlight their ability to thrive in moist environments such as medical equipment or wounds. Vigilance is crucial to prevent these opportunistic invaders from causing harm. Shifting our attention back to MRSA bacteria, SEM image C016/9422 showcases its distinctive appearance. The menacing spikes on its surface symbolize the potential danger lurking within hospitals and clinics worldwide. Understanding this enemy is vital in combating its spread effectively. Adjacent to it lies another SEM image labeled C016/9421—another glimpse into the world of MRSA bacteria. With each magnification level revealing more details about these microorganisms' structure and behavior, scientists strive towards finding innovative solutions that can outsmart them. Amongst Staphylococcus aureus MRSA strains emerges an intriguing cluster represented by images C013/9375, 6215, 6216, and 6214 under different conditions. Each variant possesses distinct characteristics that contribute to their virulence and persistence within healthcare facilities. These captivating visuals remind us of the unseen threats present in hospital environments—the silent battles fought daily against nosocomial infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus MRSA strains alike.