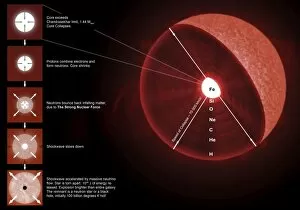
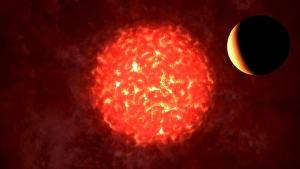
Neutron Stars Collection
Neutron stars, the remnants of massive stars that have gone supernova, are truly fascinating celestial objects
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
Neutron stars, the remnants of massive stars that have gone supernova, are truly fascinating celestial objects. Imagine a red giant star orbiting a black hole, an awe-inspiring sight in itself. In the Cygnus X-1 system, an artist's illustration captures this cosmic dance between two powerful entities. Speaking of supernovae, witnessing the final stages of a massive star's life is nothing short of spectacular. An illustration vividly portrays the explosive moment when a massive star goes supernova, releasing unimaginable amounts of energy into space. One such example is the Crab Nebula, a mesmerizing remnant from a supernova explosion observed by ancient civilizations. Its intricate structure and vibrant colors continue to captivate astronomers and stargazers alike. To put things into perspective, consider our humble Earth compared to other stellar bodies like the sun or even smaller ones like white dwarfs and neutron stars. The contrast is mind-boggling. But what if we delve into more extreme scenarios? Picture Earth being devoured by a black hole; it symbolizes both our fascination with these cosmic phenomena and our fear of their immense power. Moving further out into space, IC 443 supernova remnant in Gemini showcases nature's ability to create breathtaking displays even after destruction has occurred. It serves as a reminder that beauty can emerge from chaos. Imagine standing on Neptune and looking back at our solar system if VY Canis Majoris replaced our Sun—a humbling experience indeed. This supergiant star would dwarf everything we know about size and scale. Venturing deeper into the Milky Way galaxy reveals its central region—an enigmatic place teeming with countless stars and mysteries waiting to be unraveled by curious minds exploring its depths. Binary star systems provide another intriguing aspect of neutron stars' existence—two stellar companions locked in an eternal gravitational embrace as they journey through space together. However, perhaps one of the most extraordinary events occurs when two neutron stars collide, merge, and form a black hole.