Monochrome Image Collection
Capturing the essence of time and history, monochrome images transport us to pivotal moments in our world
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
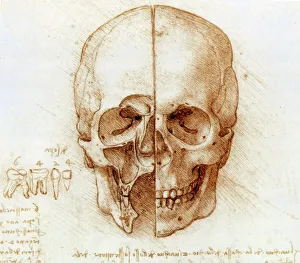
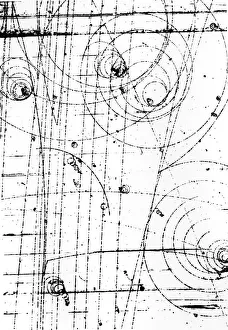
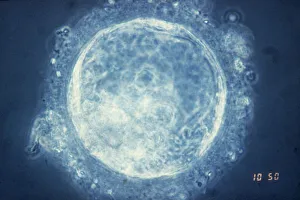
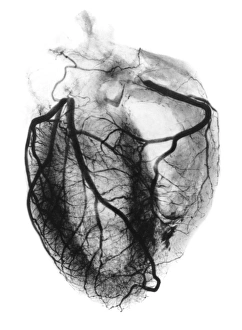
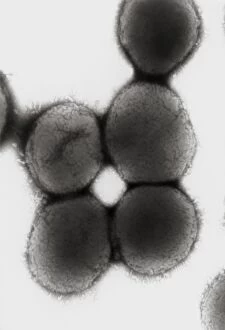
Capturing the essence of time and history, monochrome images transport us to pivotal moments in our world. From Leonardo da Vinci's intricate study of skull anatomy to the mesmerizing bubble chamber photo capturing sigma particle decay, these black-and-white snapshots unveil the beauty hidden within simplicity. The Apollo 17 astronaut's silhouette against the lunar landscape and the iconic footprints left on the Moon remind us of mankind's extraordinary achievements beyond Earth's boundaries. As night falls, a breathtaking view reveals Europe illuminated like never before, while scientists' first observation of the omega-minus particle unravels mysteries at a subatomic level. Delicate as life itself, a monochrome image unveils humanity's earliest stages with a glimpse into a human blastocyst. In contrast, Humphry Davy stands larger than life in his caricature portrait, symbolizing scientific innovation and discovery. Witnessing nature's marvels is equally captivating; an immense European starling flock takes flight in perfect harmony under an endless sky. Gazing up at a full moon or witnessing a total solar eclipse on that fateful day in March 2006 evokes awe-inspiring wonder for celestial wonders that transcend time and space. Finally, Marie Curie graces us with her presence through her caricature portrait—a reminder of her groundbreaking contributions to science and radiation research, and are not just pictures; they are portals connecting past triumphs, present explorations, and future aspirations.