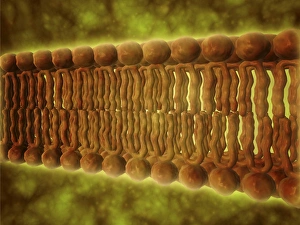
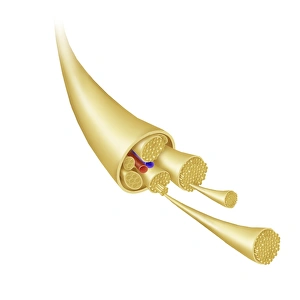
Molecular Biology Collection
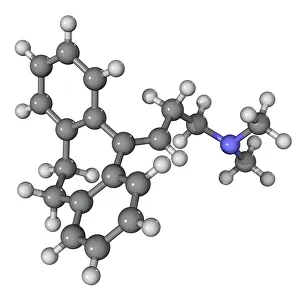
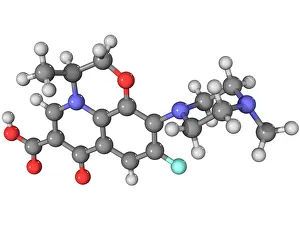
"Molecular Biology: Unveiling the Secrets of Life at a Microscopic Level" Amitriptyline Antidepressant Molecule: Exploring the Chemical Pathways to Mental Well-being
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
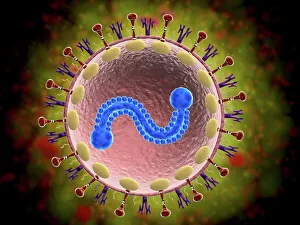
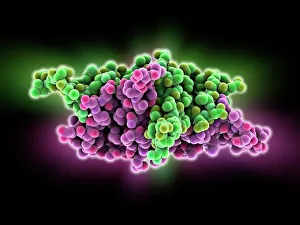
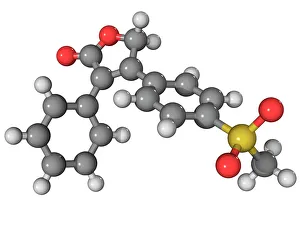
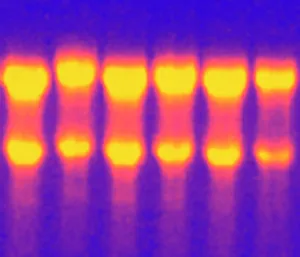
"Molecular Biology: Unveiling the Secrets of Life at a Microscopic Level" Amitriptyline Antidepressant Molecule: Exploring the Chemical Pathways to Mental Well-being. Watson and Crick, DNA Discovers: Pioneers Who Unraveled the Double Helix Structure, Revolutionizing Genetics. Creatine Amino Acid Molecule: Fueling Muscles and Unlocking Athletic Performance Potential. Microscopic View of Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus: Understanding the Culprit Behind Common Respiratory Infections. Embryo Development 24-36 Hours After Fertilization: Witnessing the Miracle of Life from Conception to Early Growth. Zinc Fingers Bound to a DNA Strand: Decoding Genetic Instructions for Cellular Functions and Disease Prevention. SARS Coronavirus Protein: Investigating Viral Mechanisms for Effective Control and Treatment Strategies. Vioxx Drug Molecule: Analyzing Medications' Molecular Structures for Enhanced Safety and Efficacy in Pain Management. Levofloxacin Antibiotic Molecule: Combating Bacterial Infections with Precision-targeted Therapies. Electrophoresis of RNA: Separating Genetic Material to Study Gene Expression Patterns in Health and Disease Mitochondrial DNA - The Powerhouses Within Our Cells Holding Clues to Evolutionary History Cone Snail Venom Component Molecule.