Microtubule Collection (page 3)
Microtubules are dynamic structures found within cells that play a crucial role in various cellular processes
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
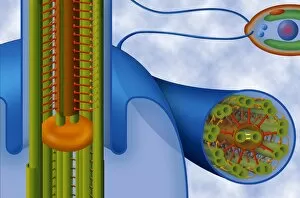
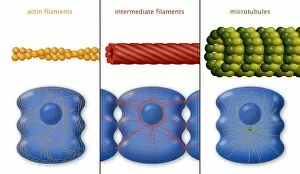
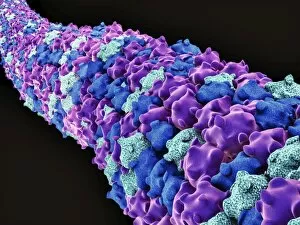
Microtubules are dynamic structures found within cells that play a crucial role in various cellular processes. In HeLa cells, these tiny tubular structures can be visualized using light micrographs C017/8299 and C017/8298, revealing their intricate network throughout the cell. During cell division, fluorescent micrographs capture the mesmerizing sight of dividing cells with microtubules orchestrating the process. These images showcase the essential role of microtubules in ensuring accurate chromosome segregation and cytokinesis. Exploring further into cell structure, artwork depicts the relationship between proteins, microtubules, and overall cellular organization. This conceptual image highlights how these protein filaments provide structural support and act as tracks for intracellular transport. In plant cells undergoing mitosis, light micrographs offer a glimpse into the fascinating world of microtubule-mediated division. The intricate dance of spindle fibers during this process ensures proper distribution of genetic material to daughter cells. Beyond traditional microscopy techniques, conceptual images shed light on other aspects related to microtubules. One such image portrays Radiolarians with a skeletal frame—a representation emphasizing how these organisms utilize intricate internal structures akin to our own cellular scaffolding. Centrioles also feature prominently in understanding microtubule function. Conceptual images depict these cylindrical structures that organize spindle fibers during cell division or serve as basal bodies for cilia and flagella formation—further highlighting their importance in cellular architecture. Lastly, a conceptual image showcases an entire plant cell along with its components—an illustration providing insight into how different organelles interact within a complex network regulated by microtubules. From HeLa cells to plant mitosis and beyond, exploring the captivating world of microtubules unveils their indispensable role in maintaining cellular integrity and driving vital processes within living organisms.