Microbes Collection
Microbes, the invisible world within us and around us, hold a captivating story of survival and impact
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
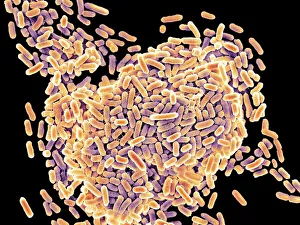
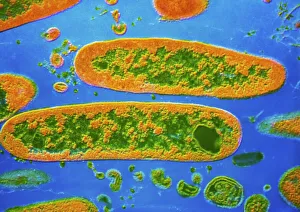
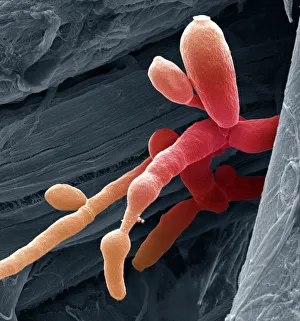
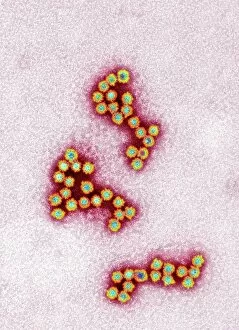
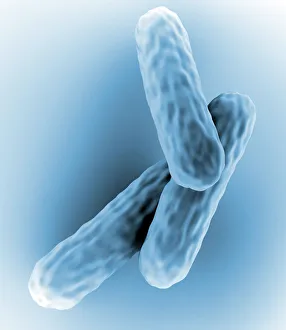
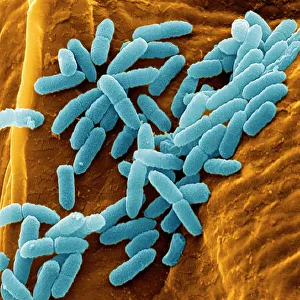
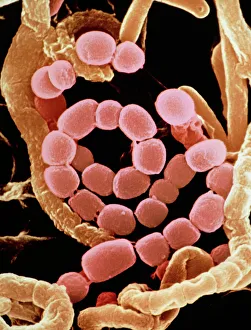
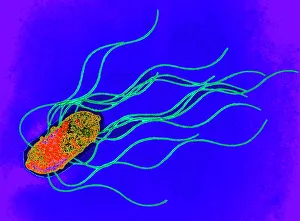
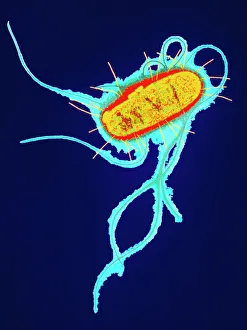
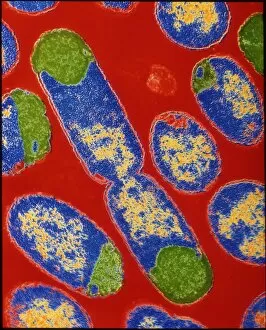
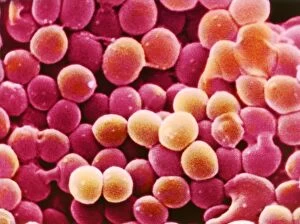
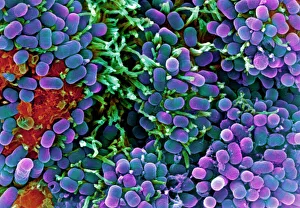
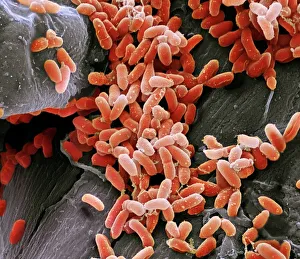
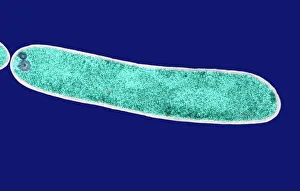
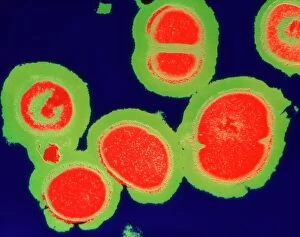
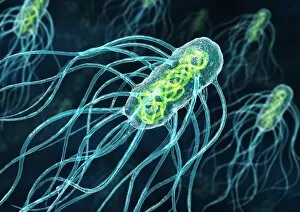
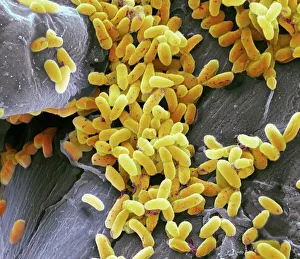
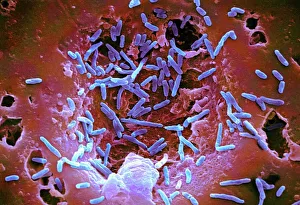
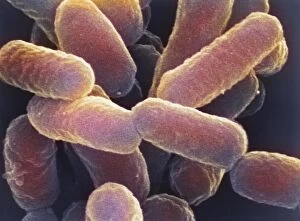
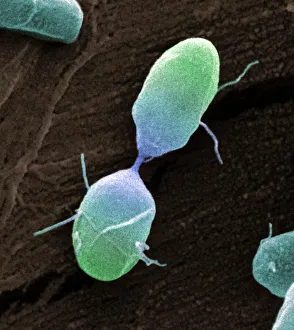
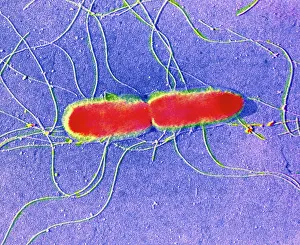
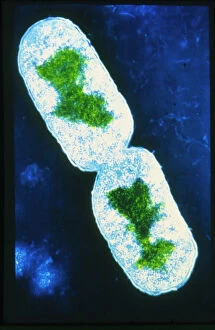
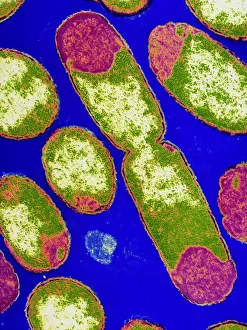
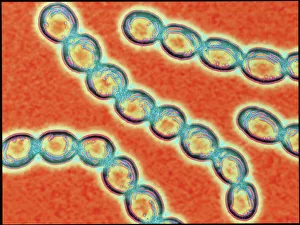
Microbes, the invisible world within us and around us, hold a captivating story of survival and impact. Through powerful imaging techniques like scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), we can explore their intricate forms and unravel their secrets. In one frame, E. Coli bacteria appear as tiny rods under SEM, reminding us of their prevalence in our gut microbiome. Another image showcases Salmonella bacteria through SEM, highlighting the potential danger they pose to our health if not handled with caution. A colored TEM image reveals Yersinia pestis bacteria responsible for the devastating plague outbreaks throughout history. The vibrant hues bring attention to the severity of this pathogen's impact on humanity. Switching gears to fungi, Candida fungus takes center stage under SEM. Its branching structures captivate our imagination as we ponder its role in infections and diseases. Anthrax cultures depicted in a historical diagram remind us of the dark chapters where bioweapons threatened lives. This visual representation serves as a reminder of how they are be harnessed for destruction or manipulated for good. Norovirus particles captured by TEM showcase their spherical shape – these minuscule agents are notorious for causing gastrointestinal distress during outbreaks. Tuberculosis bacteria come into focus next; their presence is marked by rod-shaped organisms that invade lung tissue silently but relentlessly affecting millions worldwide each year. Spiral spore chains formed by Streptomyces bacteria create an enchanting pattern when observed through microscopic lenses. These soil-dwelling microorganisms contribute significantly to antibiotic production while shaping ecosystems beneath our feet. Flagellate bacteria display elegance with their whip-like appendages propelling them forward towards new habitats or resources - an evolutionary marvel worth contemplating upon seeing them up close under SEM once again. Lastly, Staphylococcus aureus bacterium reminds us that even seemingly harmless species can turn deadly when given the opportunity to cause infections if left unchecked within vulnerable individuals' bodies. Microbes, whether they be E.