Micro Biology Collection (page 4)
Microbiology is a fascinating field that delves into the intricate world of microscopic organisms
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
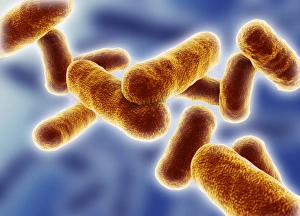
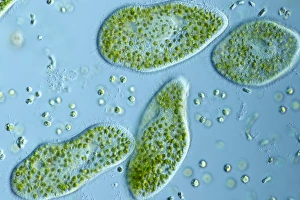
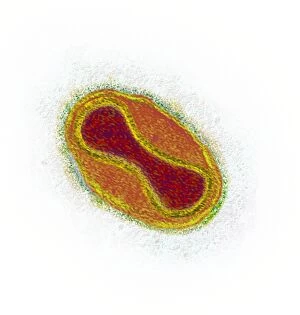
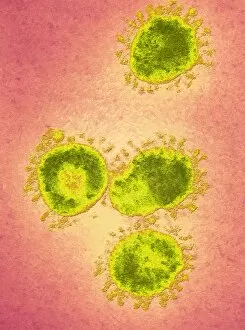
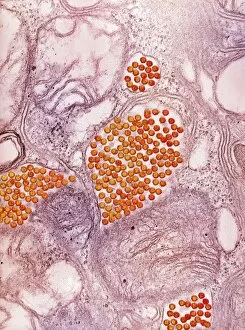
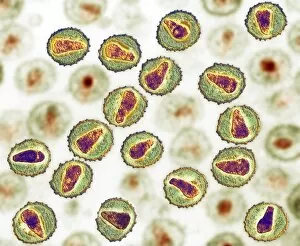
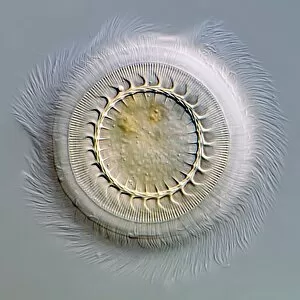
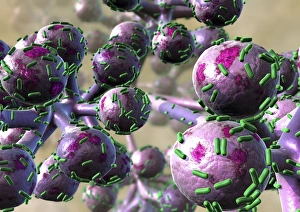
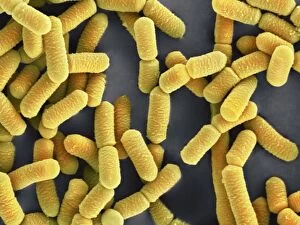
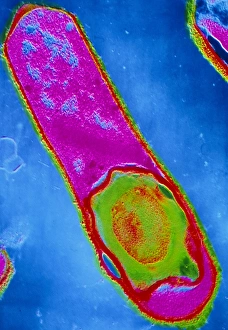
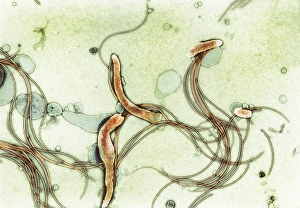
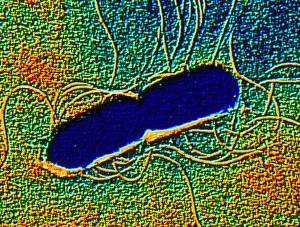
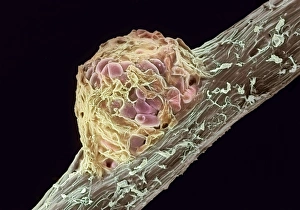
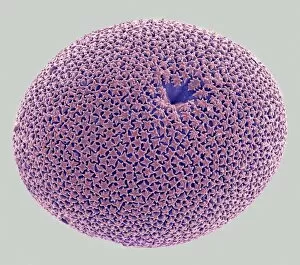
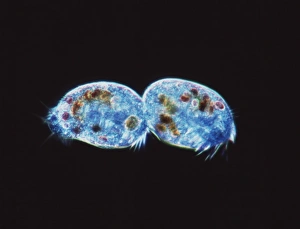
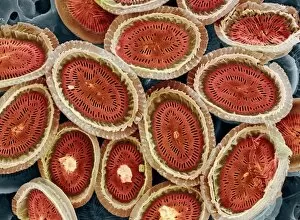
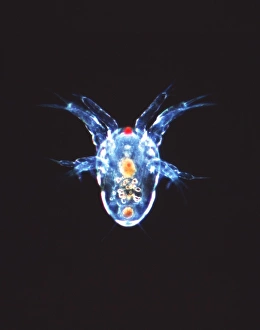
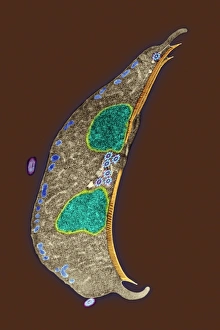
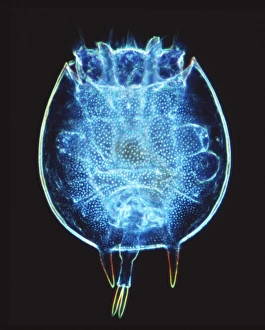
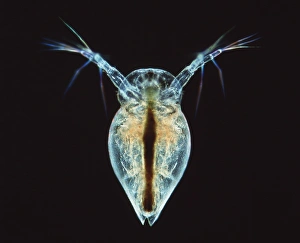
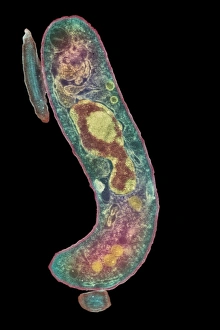
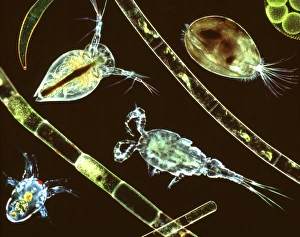
Microbiology is a fascinating field that delves into the intricate world of microscopic organisms. From budding yeast cells to calcareous phytoplankton, these tiny beings hold immense importance in our ecosystem. Take a closer look through the lens of a scanning electron microscope (SEM), and you'll be amazed by their intricate structures. One such example is the avian flu virus, which can cause devastating outbreaks among bird populations. Its unique shape and composition are revealed under SEM, highlighting its potential threat to both animals and humans alike. Diatoms, another group of microorganisms, showcase stunning beauty when observed through SEM. Their delicate silica shells form intricate patterns that resemble works of art. These diatoms play a crucial role in marine ecosystems as primary producers. E. coli bacteria, often associated with foodborne illnesses, reveal their rod-shaped structure under SEM. Understanding their morphology helps scientists develop strategies to combat infections caused by this notorious bacterium. The PSCI2A-00015 embryonic stem cell captured under SEM demonstrates its incredible regenerative capabilities. This versatile cell type holds great promise for future medical advancements and treatments. Salmonella bacteria also come into focus under SEM, displaying their flagella-covered surface responsible for motility and infection transmission. Studying these pathogens aids in developing effective prevention measures against salmonellosis. Intriguingly colored TEM images unveil Yersinia pestis bacteria responsible for causing deadly diseases like bubonic plague throughout history. Unveiling their detailed structure allows researchers to better understand how they function within host organisms. Another captivating diatom species reveals itself through SEM imaging - showcasing nature's artistic side once again. These single-celled algae contribute significantly to global carbon fixation while providing habitats for countless aquatic creatures. Candida fungus captures attention with its filamentous appearance when viewed at high magnification using SEM techniques. This opportunistic pathogen can cause various infections in humans ranging from mild oral thrush to life-threatening systemic infections.