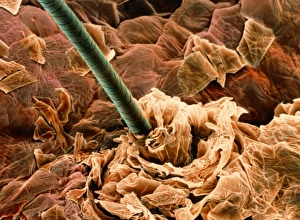
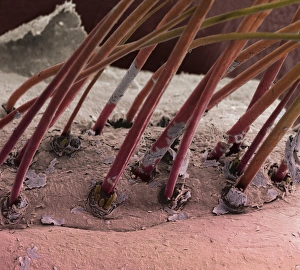
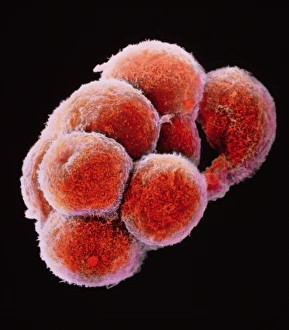
Magnified Image Collection
"Exploring the unseen wonders of the microscopic world: from particle tracks to intricate tissues and beyond
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
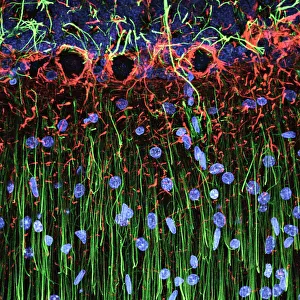
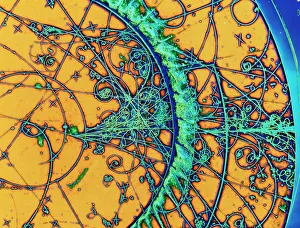
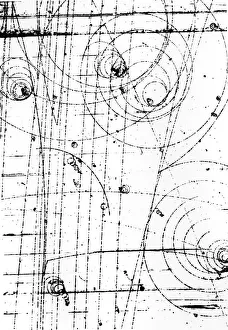
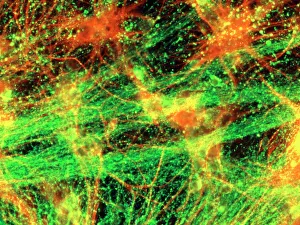
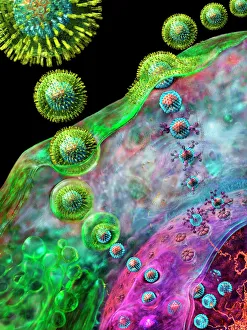
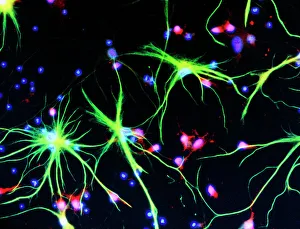
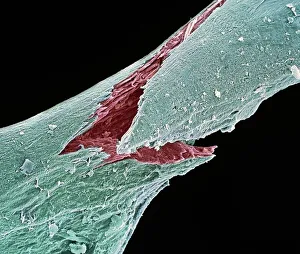
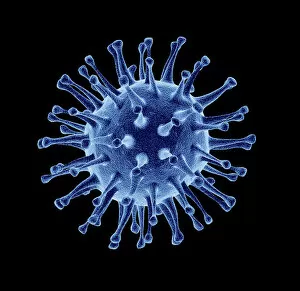
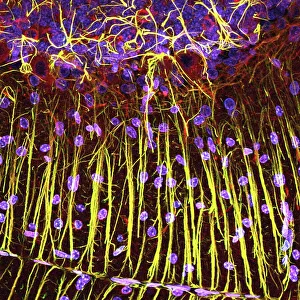
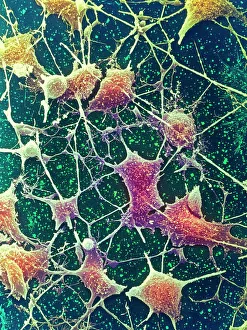
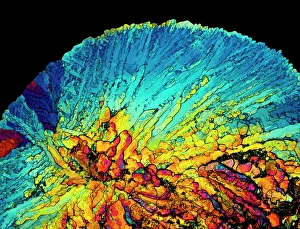
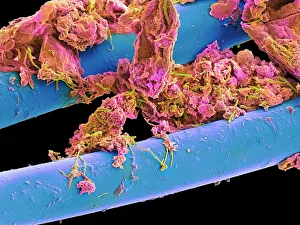
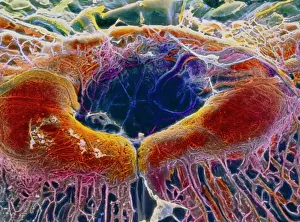
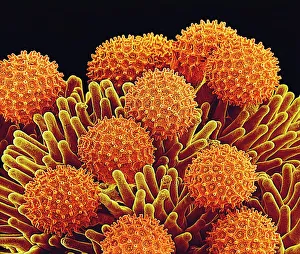
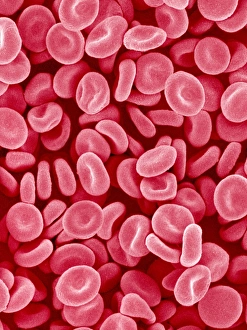
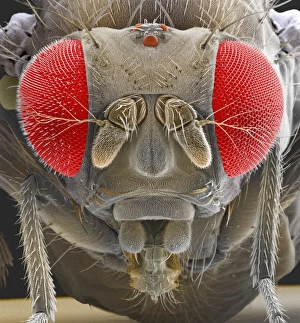
"Exploring the unseen wonders of the microscopic world: from particle tracks to intricate tissues and beyond. " "Unveiling the hidden beauty within: a closer look at cerebellum tissue through a mesmerizing light micrograph. " "A captivating glimpse into the mysteries of subatomic particles: behold the bubble chamber photo capturing sigma particle decay. " "The groundbreaking moment in science history: witness the first observation of omega-minus particle, forever changing our understanding of matter. " "Awe-inspiring beginnings: marvel at the intricate structure of a human blastocyst, where life takes its first steps. " "Diving deep into neural networks: an illuminating immunofluorescent LM reveals stunning neurons and astrocytes in all their glory. " "Unraveling nature's cycle within us: witness the uterus lining during menstruation, as seen through SEM imaging - a fascinating display of renewal and change. " "Peering into viral threats that loom above us all: explore avian flu virus up close, revealing its complex structure and potential dangers it holds. " "The crystalline beauty behind love and bonding: discover oxytocin hormone crystals under PLM C016 / 7196 microscopy - nature's secret ingredient for connection. " "A tapestry woven by nature itself: delve into intricately detailed fabric structures captured through SEM imaging - artistry on a microscopic scale. " "Glimpsing into windows to our souls with breathtaking precision: explore the iris of an eye like never before, revealing unique patterns that make each person truly one-of-a-kind. " "Revealing fragility beneath strength: examine osteoporotic bone under SEM, shedding light on this silent disease affecting millions worldwide.