Magnetic Resonance Imaging Collection (page 4)
"Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Unveiling the Intricate Pathways of the Human Brain" The wonders (MRI) have revolutionized our understanding of brain anatomy and function
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
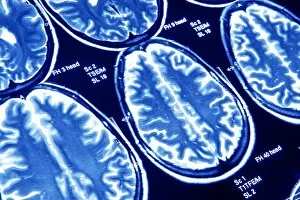
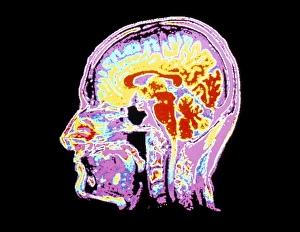
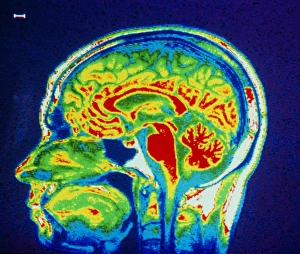
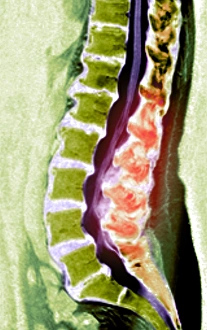
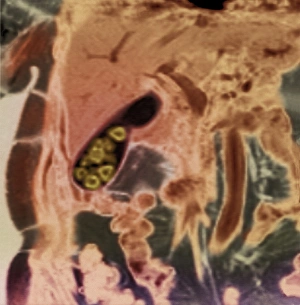
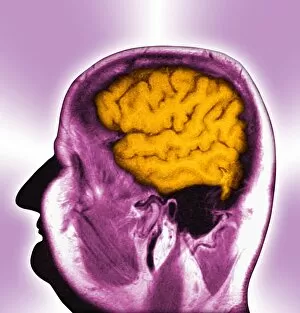
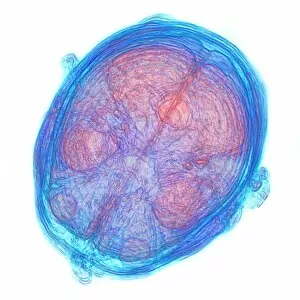
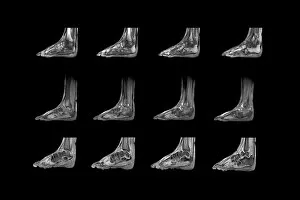
"Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Unveiling the Intricate Pathways of the Human Brain" The wonders (MRI) have revolutionized our understanding of brain anatomy and function. Through advanced techniques like diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), MRI scans provide a window into the complex network of brain fibres, allowing us to explore the intricate pathways that shape our thoughts, emotions, and actions. In DTI MRI scan C017/7099 and C017/7035, we witness the mesmerizing white matter fibres crisscrossing throughout the human brain. These delicate structures serve as highways for information transmission, connecting different regions and facilitating efficient communication within our neural circuitry. But MRI is not limited to studying healthy brains alone. In images like C014/5666 and C014/5668, we delve deeper into neurological conditions such as bacterial meningitis or ruptured breast implants. By examining these abnormalities through MRI scans, medical professionals gain valuable insights into diagnosis and treatment planning. However, it's not just diseases that captivate researchers' attention; normal brain MRIs also offer fascinating glimpses into our cognitive prowess. With each healthy brain scan captured by this remarkable technology, we uncover more about how these intricate networks contribute to memory formation, problem-solving abilities, creativity, and so much more. Beyond neuroscience applications lies another realm where MRI proves invaluable – orthopedics. Images like C018/0649 showcase its ability to visualize injuries such as a ruptured Achilles tendon with unparalleled clarity. This non-invasive technique aids in accurate diagnoses while guiding effective treatment strategies for patients seeking relief from musculoskeletal ailments. Magnetic resonance imaging has truly transformed medicine by providing detailed snapshots of both normalcy and pathology across various fields – be it neurology or orthopedics. As scientists continue pushing boundaries in research using this powerful tool, humanity gains an ever-deepening understanding of ourselves - unlocking mysteries hidden within the mesmerizing white matter fibres of the human brain.