La Ferrassie 1 Collection
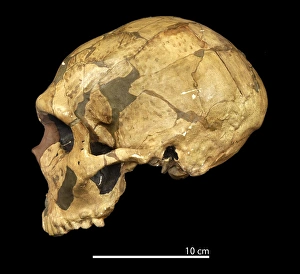
"La Ferrassie 1: Unraveling the Enigma of Neanderthals" The discovery of La Ferrassie 1, a remarkable Homo neanderthalensis cranium
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
"La Ferrassie 1: Unraveling the Enigma of Neanderthals" The discovery of La Ferrassie 1, a remarkable Homo neanderthalensis cranium, has provided invaluable insights into our ancient human ancestors. This fossilized skull, found in the famous La Ferrassie cave in southwestern France, offers a glimpse into the lives of Neanderthals who roamed the Earth over 40, 000 years ago. With its robust features and distinct cranial shape, La Ferrassie 1 stands as a testament to the unique characteristics that defined this extinct species. The study of this specimen has shed light on their physical attributes and evolutionary history. Comparisons with other hominin fossils such as Homo erectus (Sangiran 17) and early Homo sapiens have revealed intriguing connections between different branches of our family tree. While some similarities can be observed between these species, it is clear that Neanderthals possessed distinctive traits that set them apart. Through meticulous analysis and reconstruction efforts using casts made from La Ferrassie 1's cranium, scientists have pieced together an image of what these ancient individuals may have looked like. Their strong brow ridges, prominent nasal cavities, and elongated skulls paint a vivid portrait of our distant relatives. Furthermore, multiple specimens discovered at La Ferrassie provide researchers with an opportunity to explore variations within the Neanderthal population. Fossil skull fragments labeled C016/0568, C016/0556, C016/0573, C016/0570, and C016/0566 offer glimpses into individual differences among these prehistoric humans. As we continue to unravel the mysteries surrounding our evolutionary past through discoveries like La Ferrassie 1's cranium cast and its counterparts from this site; we gain valuable knowledge about how humanity evolved over time. These findings contribute to our understanding not only of Neanderthals but also of our own species, Homo sapiens.