Kepler Collection
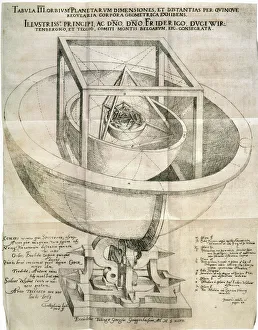
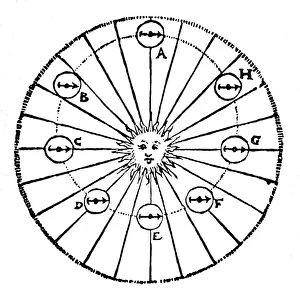
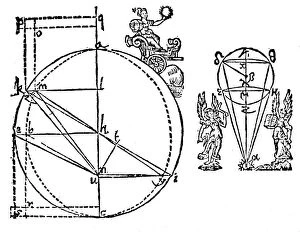
"Exploring the Mysteries of the Universe: Kepler's Legacy" In 1596, Johannes Kepler unveiled his groundbreaking model of the universe in his Mysterium Cosmographicum
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
"Exploring the Mysteries of the Universe: Kepler's Legacy" In 1596, Johannes Kepler unveiled his groundbreaking model of the universe in his Mysterium Cosmographicum. This line engraving depicted a mesmerizing Full Moon, captivating minds with its celestial beauty. Kepler's revolutionary ideas extended beyond mere illustrations. His meticulous observations and mathematical calculations led to the development of the Kepler Planetary System, which transformed our understanding of planetary motion. One notable discovery attributed to the exoplanet Kepler-10b. Through artistic renditions, we can envision this distant world, sparking curiosity about its unique characteristics and potential for life. Beyond his scientific achievements, Johannes Kepler had an intriguing connection with Emperor Rudolf II. Their collaboration fostered an environment where knowledge flourished and astronomical advancements thrived. From Tamworth B79 8 Map to Johann Scheuchzer's planet orbit C008/8008 in 1731, references to Kepler's work continue to inspire generations of astronomers worldwide. His contributions have left an indelible mark on our understanding of space and time. Even today, we honor Johannes Kepler as a brilliant German mathematician whose brilliance transcends time. His legacy lives on through countless scientists who follow in his footsteps, pushing boundaries and unraveling new cosmic mysteries. As seen in Burroughs' depiction at the Paris Exhibition of 1889 or Wellcome Chemists' admiration for him throughout history – from art exhibitions to scientific conferences – it is evident that Kepler remains a symbol of inspiration for those seeking answers about our vast universe. Let us celebrate Johannes Kepler's enduring legacy as we gaze upon a radiant Full Moon tonight – a reminder that there are still infinite wonders waiting to be discovered among the stars he so passionately studied centuries ago.